Understanding Database Management
There are many methods to manage databases and access them securely through database users. ServerAvatar supports MySQL, MariaDB, and MongoDB, and manages them in a consistent, secure way. It is possible that your previous management system managed the database differently from ServerAvatar.
Therefore, understanding database and access management is very important if you are just getting started with ServerAvatar.
In ServerAvatar, database management is designed for simplicity and security. For SQL databases (MySQL and MariaDB), users are isolated to a single database. For MongoDB, access is similarly restricted to the assigned database, ensuring strong isolation across all supported engines.
Here is a visual representation of database management in ServerAvatar.
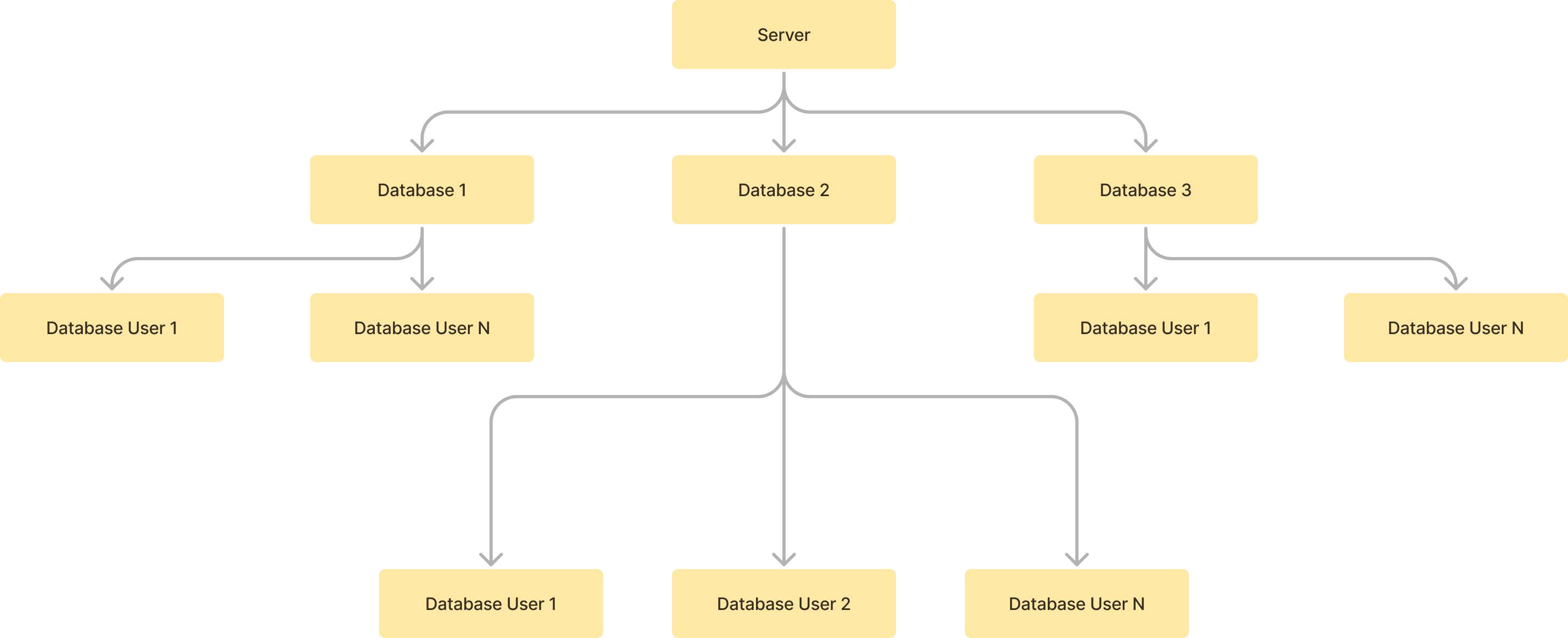
In this diagram, there are multiple SQL databases (MySQL or MariaDB) on a single server. MongoDB follows the same principle of user-to-database isolation, although its access model is document-based instead of table-based. Then, there are multiple database users for a single database. Usually, when you create a database in ServerAvatar (MySQL, MariaDB, or MongoDB), you will also be asked to create a user for that database.
That user will have full access to the assigned database only. Or, you can say that a database user belongs to the database. It means that the database user's credentials cannot be used to manipulate or see the data on other databases hosted on the same server.
You can have as many database users as you want under any specific database. You can also create database users with a remote host (IPv4) to enable remote access for MySQL and MariaDB. For MongoDB, remote access is supported with proper authentication and firewall rules. You can learn more about it in the "Create Database User" section.