
When it comes to optimizing PHP performance on your web server, PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) plays a vital role. But here’s where things get a bit technical—and often confusing choosing the right Process Manager type: ondemand, dynamic, or static.
Think of PHP-FPM like a restaurant kitchen. The Process Manager type decides how many cooks (PHP workers) are working at any given time. Do you always keep cooks ready (static)? Call them only when needed (ondemand)? Or keep a few ready and call more as needed (dynamic)? Choosing the wrong setup can either waste your server’s resources or slow down your site during traffic spikes.
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know—step-by-step, in simple language, with examples and tips—so you can make the right decision for your server. Whether you’re managing your own VPS, using platforms like ServerAvatar, or just want to understand what goes on under the hood, this guide is for you.
What is PHP-FPM?
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is an advanced PHP handler that improves performance and resource management. Instead of creating a new PHP process for every request (which is slow and inefficient), PHP-FPM keeps processes alive to handle requests faster.
It’s like having staff on standby to serve food immediately, rather than hiring them every time someone orders.
Why Does the Process Manager Type Matter?
The process manager type decides how many PHP processes run on your server and how they’re managed. This affects:
- Performance under traffic
- Memory usage
- CPU consumption
- Server cost (on cloud platforms)
Choosing the right type ensures your website is fast, responsive, and doesn’t overload your server.
Overview of PHP-FPM Process Manager Types
There are three main types:
- static – Fixed number of PHP workers
- dynamic – Automatically scales between min and max workers
- ondemand – Spawns PHP workers only when needed
Each type has different use-cases and benefits. Let’s look at them in detail.
Static Process Manager Explained
Static keeps a fixed number of PHP processes running at all times.
How it works:
- You define pm.max_children
- That exact number of PHP workers always stay active
- No auto-scaling
Use Case:
Ideal for dedicated servers with plenty of RAM and predictable traffic.
Example:
pm = static
pm.max_children = 10You’ll always have 10 PHP workers, even if only one user visits the site.
Pros:
- Predictable performance
- No process creation delay
Cons:
- Wastes memory when traffic is low
- Not ideal for shared servers
Dynamic Process Manager Explained
Dynamic is the default and most flexible option.
How it works:
You set:
- pm.max_children
- pm.start_servers
- pm.min_spare_servers
- pm.max_spare_servers
- PHP workers scale between min and max values depending on traffic.
Example:
pm = dynamic
pm.max_children = 20
pm.start_servers = 5
pm.min_spare_servers = 3
pm.max_spare_servers = 10
Use Case:
Perfect for general-purpose servers, shared hosting, and sites with variable traffic.
Pros:
- Efficient memory usage
- Good performance under varying load
Cons:
- Slight overhead when scaling processes

Ondemand Process Manager Explained
Ondemand spawns PHP processes only when needed, then kills them after a timeout.
How it works:
Set:
- pm.max_children
- pm.process_idle_timeout
- Processes are created on request and removed after being idle.
Example:
pm = ondemand
pm.max_children = 20
pm.process_idle_timeout = 10s
Use Case:
Best for low-traffic or bursty applications, like admin panels or APIs.
Pros:
- Minimal memory usage
- Saves resources when idle
Cons:
- Slow on first request due to process creation
- Not great for high concurrency
Comparison: ondemand vs dynamic vs static
| Feature | Static | Dynamic | Ondemand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Always active processes | ✅ | ⚠️ (some) | ❌ |
| Memory-efficient | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Performance under load | ✅ | ✅✅ | ❌ |
| Best for low traffic | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Requires tuning | ❌ | ✅✅ | ✅✅ |
Analogy:
- Static is like keeping all lights on 24/7
- Dynamic is like motion-sensor lights
- Ondemand is like turning on lights only when someone presses a switch
Choosing the Right Type for Your Server
Use this quick guide:
- Use static for high-performance, dedicated environments
- Use dynamic for most typical web servers
- Use ondemand for low-traffic, admin panels, or APIs
Ask yourself:
- Does your site get consistent traffic?
- Are you limited by memory?
- Do you prioritize speed or efficiency?
How to Check Current PHP-FPM Settings
if you are using serverAvatar
What is ServerAvatar
ServerAvatar is a cloud management platform that lets you easily set up, manage, and monitor cloud servers for hosting websites and applications.
It supports automatic server configuration, app deployment, SSL setup, backups, monitoring, and more — without needing complex terminal commands.
It also now provides cloud hosting and servers, so you can both host and manage your projects from one place.
Steps:
Log in to your ServerAvatar Dashboard.
Select your server from the server list. go to your application In the left menu
Click PHP Setting
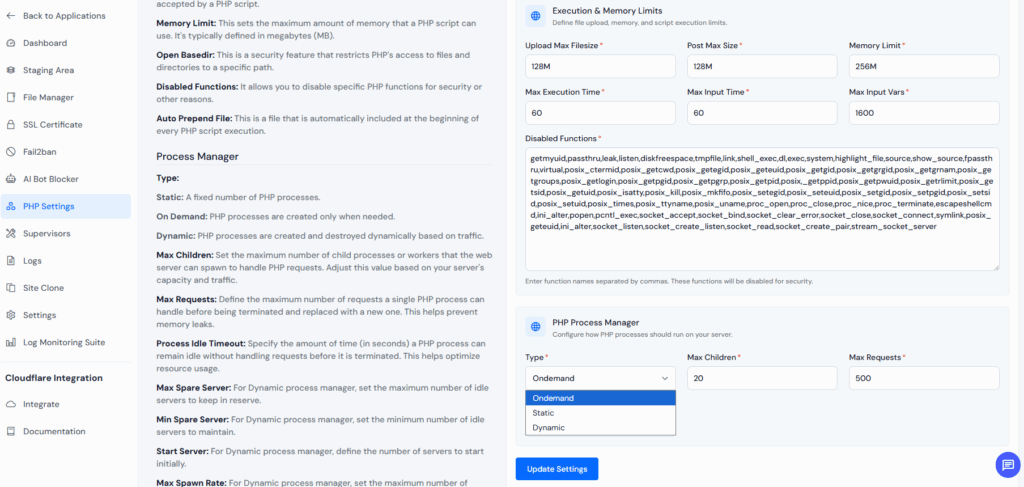
Locate Process Manager and select your preferred type:
To find out which Process Manager your server is using:
ondemand
dyanamic
static
Click Save Changes to apply settings.
ServerAvatar will automatically reload PHP-FPM with your new configuration.
With Command Line:
Step-by-Step:
SSH into your server
Run:
grep -i pm /etc/php/*/fpm/pool.d/*.confLook for pm =, pm.max_children, etc.
How to Change PHP-FPM Process Manager Type
Step-by-Step:
- Edit your PHP-FPM pool file (usually at /etc/php/8.1/fpm/pool.d/www.conf)
- Change:
pm = ondemand3. Adjust other settings like max_children or process_idle_timeout
4. Restart PHP-FPM:
sudo systemctl restart php8.1-fpmTip: Always back up your config before making changes.
Best Practices for PHP-FPM Configuration
- Monitor traffic to understand load patterns
- Use dynamic as a safe default
- Tweak settings based on memory availability
- Avoid setting pm.max_children too high (can cause OOM errors)
- Combine with tools like NewRelic, htop, or ServerAvatar Monitoring
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Using static on small VPS → High RAM usage
- Setting ondemand without tuning process_idle_timeout → Performance lags
- Forgetting to restart PHP-FPM after config changes
Performance Tips and Monitoring Tools
Recommended Tools:
- ServerAvatar: Graph-based usage insights
- top or htop: Real-time process monitoring
- nginx access logs: Check request volume
- PHP-FPM status page: Shows real-time worker usage
Conclusion
Choosing between ondemand, dynamic, and static isn’t just about toggling a setting—it’s about aligning your PHP server configuration with your actual traffic needs and resource availability.
Dynamic is best for most users.
Static suits high-performance needs.
Ondemand is great for saving resources.
With tools like ServerAvatar, managing and switching between these types becomes a breeze. Use this guide to make informed decisions and ensure your server runs smoothly, efficiently, and quickly.
