
Latency plays a major role in how quickly a website loads. Have you ever clicked on a website and waited… and waited… and waited for it to appear? Frustrating, right? While many things can cause a slow-loading website, one of the biggest, and most overlooked, reasons is server location.
Imagine ordering food from your neighborhood restaurant versus one across the country. Which one will arrive faster? The same reasoning applies to the data on your website. It takes longer the farther away the server is from the visitor.
In this blog, we’ll go over all you need to know about how the location of a server affects latency. No complicated tech terms, just real, human-friendly information.
What does latency mean?
Latency is the amount of time it takes for data to go from a server to your device and back. Generally, it is measured in ms (milliseconds). The reaction time gets faster as the latency goes down.
Let’s say you click on a website. That click sends a request to a server. The server responds by sending data back to your browser. The round-trip time is your latency.
What Is Server Location?
Server location refers to the physical place where your web server is hosted. It could be in Mumbai, New York, London, or anywhere else in the world.
Just like you wouldn’t want your pizza to come from another country, you don’t want your server to be too far from your users.
How Server Location Impacts Latency
The farther away the server is from the user, the longer it takes for data to travel. This increases latency.
For example:
- A person in India who connects to a server in the U.S. might have a latency of 250ms.
- The same user could have a latency of only 30 ms when connecting to a server in Mumbai.
That is major difference in how fast loads website!
Latency as a Delivery Route in Real Life
Think about writing someone a letter:
- Nearby location: The letter gets there the next day if it’s close by.
- Across the globe: It could take a week.
The same goes with latency. It takes time for information to get to you, as if route is longer. Your server is like the post office, and your website is like that letter.
To understand how server location impacts latency, let me show you a quick comparison between two of the most visited websites in the world, Google and Facebook.
By testing the latency to both websites, you can observe noticeable differences in response times. These differences are often influenced by the geographical location of their nearest data centers, network routing, and overall server infrastructure.
This simple comparison helps highlight how physical distance and server optimization can affect the speed at which websites respond to user requests.
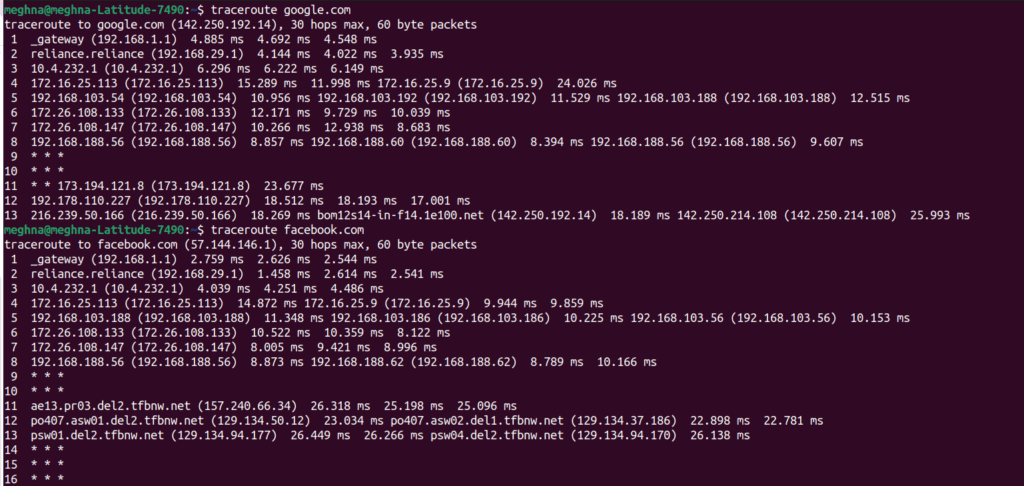
As you can see in the above attached screenshot, the traceroute results show that Google’s servers responded slightly faster than Facebook’s, with lower latency and fewer hops overall. This indicates that Google’s network path is more optimized or geographically closer in this case.
Why Websites Need to Be Fast
Did you know that:
- 53% of consumers would leave a site if it takes longer than three seconds to load.
- Customers, trust, and confidence are lost when your websites gets slow.
Latency has a direct impact on how fast a page loads. Even a well-designed site may feel slow if your server is far away.
Server Location vs Hosting Type
Not all hosting is created equal.
- Shared Hosting: More than one website uses the same server. The location will be set.
- VPS (Virtual Private Server): You have more control, such as where the server is located.
- Cloud Hosting: Lets you choose the region of your server most of the time.
Pro Tip: It’s easy to choose during which your server is located and manage it well with platforms like ServerAvatar.
What DNS and Routing Do
Your browser first asks the DNS (Domain Name System) where your website is before it communicates to a server.
Sometimes, even if the server is nearby, slow DNS or bad routing can make things take longer. Another technique to lower latency is to improve DNS and routing pathways.

Impact on SEO and User Experience
Google considers page speed as a ranking factor. If your server is too far from your users:
- Your site loads slower.
- Bounce rates go up.
- Search rankings drop.
Also, users tend to trust and stay longer on fast-loading websites.
Server Location and Mobile Users
Mobile users are everywhere, and often on slower networks.
- High latency + mobile data = even worse experience.
This makes it even more crucial for mobile-first websites or apps to have their servers in the right place.
How to Pick the Best Server Location
Think about
- Where most of my traffic is coming from.
- Am I trying to reach people in a certain country or area?
- Do I use a platform that allows me choose where my servers are?
It’s that easy: don’t host your server in the U.S. if your audience is in Europe.
CDN (Content Delivery Network) to the Rescue
A CDN is like having a lot of small servers all around the world. It keeps copies of your website in memory and sends them to the user from the closest location. CDNs lower latency, speed up connections, and increase uptime, especially for people all around the world.
Some well-known CDNs are:
- Cloudflare
- Amazon CloudFront
- Akamai
Ways to Lower Latency Without Moving Your Server
Can’t relocate your server? No issue.
Here are some tips:
- Use a CDN
- Optimize images and files
- Allow compression, such as GZIP
- Use caching plugins or cache on the server side
- Reduce third-party scripts
These changes can make latency much reduced, even if your server is far away.
Hosting in multiple regions and balancing the load
Using multi-region hosting is another way to cut down on latency. This means putting your program on servers in multiple data centers around the world.
How it helps:
- Users can connect to nearest data center to them.
- Makes failover happen faster if one server goes down.
- Works well with load balancing to spread out traffic.
This configuration is great for SaaS organizations, big web apps, and platforms that work all over the world.
What ServerAvatar Does to Help with Performance
With ServerAvatar, managing your server’s performance is simple. ServerAvatar makes server and application hosting and management easy and straightforward. You can directly create and deploy directly from ServerAvatar platform on DigitalOcean and Vultr platforms, and Linode, and Hetzner are coming soon, so no need for a cloud provider account
- Choose the ideal server location with supported providers and create a server directly from ServerAvatar; no cloud provider account is needed.
- Monitor latency and performance.
Whether you’re tech-savvy or just starting out, ServerAvatar helps you to host and manage your servers and applications.
Things You Should Know
- Latency is the time it takes for data to get from one place to another.
- The location of your server is important; the closer it is to users, the faster your site will be.
- Use things like CDNs, clever DNS, and performance optimization.
- Platforms like ServerAvatar make this process easier by letting you control where your server sits and how well it works.
FAQs
1. How long should it take for a webpage to load?
Latency that is less than 100ms is usually good. The lower, the better. For high-performance websites, it should be less than 50ms.
2. After I set up my server, can I move it to a different location?
Yes, you may set up a new server in a different place and move your site there utilizing cloud providers and platforms like ServerAvatar.
3. Does server location affect only latency?
Primarily, yes. But it also impacts data privacy laws, SEO rankings, and user trust if your server is in a different country.
4. How can I find out how long it takes for my website to load?
You can use tools like:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- GTMetrix
- Pingdom
They display latency, server response time, and other performance measures.
5. Is it better to use a CDN than to move your server?
Not all the time. CDNs are good for the whole world, but if most of your users are in one area, it’s better to choose a server that is close by.
Your site should be like your favorite food delivery: quick, local, and delicious.
You can provide your users the speed and experience they deserve by picking the proper server location and managing latency well.
Conclusion
The location of the server has a clear and irrefutable effect on latency, which in turn affects SEO, user experience, and conversions. Choosing the correct server location is the first step in optimizing performance, even though there are many other ways to do it.
Always think about where your audience is when you manage a blog, an online store, or a complicated SaaS application. If you use clever server placement along with tools like CDNs, load balancers, and performance monitoring, you’ll be well on your way to giving people digital experiences that are lightning-fast.
ServerAvatar is the best way to host and manage your servers without any trouble. It lets you easily deploy and manage your servers and optimize them.
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
