
Imagine your website’s main server as a central library located far away. Every time a reader (a user) anywhere in the world wants a book (a piece of content, like an image or a script), they must send a request all the way to this library. The farther the reader is, the longer the wait time. This delay, known as latency, is the arch-nemesis of website speed. So, what is CDN and how does it help? A Content Delivery Network (CDN) stores copies of your content in multiple locations worldwide, reducing latency and delivering content to users faster, no matter where they are.
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) acts as a global network of strategically positioned, smaller, specialized libraries, called Points of Presence (PoPs) or edge servers. It’s the essential infrastructure that transforms that single, far-flung library into a worldwide network of distribution centers.

When a user visits your site, the CDN intercepts the request and plays the role of a hyper-efficient traffic director. Instead of forcing the request to trek across continents to your origin server, it routes the user to the closest edge server in their geographical region.
Popular CDN Providers
Cloudflare
- Offers a comprehensive free tier.
- Known for strong security features (DDoS protection, WAF, etc.).
Amazon CloudFront
- Integrates seamlessly with AWS services.
- Highly scalable and reliable for global delivery.
Fastly
- Focuses on real-time content delivery.
- Popular for streaming, dynamic sites, and developer-friendly APIs.
KeyCDN
- Simple pricing with pay-as-you-go model.
- Provides global reach at affordable rates.
MaxCDN (StackPath CDN)
- Easy setup with strong performance.
- Flexible pricing and good for small to mid-sized businesses.
How the CDN Wins the Race Against Lag
The magic of a CDN, and its primary method for drastically improving website speed, lies in caching and proximity.
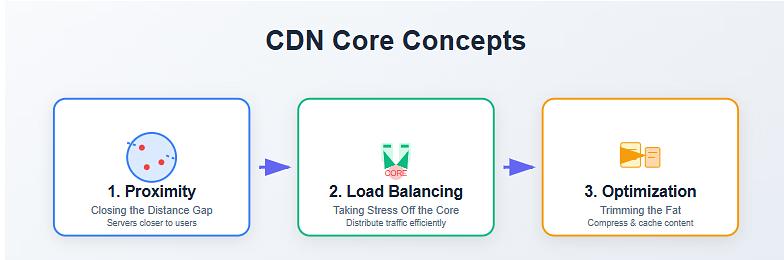
1. Proximity: Closing the Distance Gap
Distance is the single biggest factor in internet speed delay. Even though data travels at the speed of light, crossing oceans and continents still takes time.
- The Relay: When the first user in a particular city or region requests an image from your site, the CDN’s local PoP fetches it from your origin server, delivers it to the user, and keeps a temporary copy, a cached file.
- The Instant Hand-Off: For every subsequent user in that same local area, the request is served directly from that nearby PoP. The data only has to travel a short distance, virtually eliminating the geographic lag. It’s the difference between mailing a letter across town versus across the world. This massive reduction in travel time, known as reduced latency, is the core reason for the perceived “instant” loading experience.
2. Offloading and Load Balancing: Taking Stress Off the Core
Every website has a finite capacity to handle traffic. When a site gets a sudden surge (like a product launch or viral moment), the origin server can get overwhelmed, slow down, or even crash.
- Traffic Distribution: Since the CDN serves the majority of static content (images, CSS files, JavaScript) from its distributed PoPs, the vast majority of traffic never hits your main server. This offloads the delivery burden.
- Surge Protection: In the event of a huge traffic spike, the CDN automatically load balances, spreading the massive influx of requests across hundreds of edge servers worldwide. This built-in redundancy ensures your site stays fast and online, even under extreme pressure, providing superb scalability.
3. Content Optimization: Trimming the Fat
Modern CDNs go beyond simple delivery; they are also sophisticated optimizers.
- Minification and Compression: The edge servers can automatically compress files (like images, CSS, and HTML) and remove unnecessary characters or spaces from code (minification). Smaller files download faster, reducing the bandwidth required for delivery.
- Intelligent Routing: CDNs employ complex algorithms to find the fastest, most efficient network path between the PoP and the end-user, often bypassing congested network segments, like a high-tech GPS for your website’s data.
In essence, a CDN transforms your website from a single, static destination into a global, rapidly accessible service, ensuring that speed and quality are maintained regardless of where your users are logging in from.

Additional Benefits Beyond Speed
While speed improvement is the primary advantage, CDNs offer several other benefits. They provide enhanced security through DDoS protection and can filter out malicious traffic before it reaches your origin server. CDNs also improve SEO rankings, as Google and other search engines factor page speed into their algorithms.
The redundancy built into CDN networks also means better uptime. If one server fails, traffic is automatically routed to other available servers, ensuring your website remains accessible even during server outages or maintenance.
FAQ’s
What is a CDN?
A globally distributed network of servers that caches web content (like images, videos, and scripts) closer to users, speeding up delivery.
How does a CDN work?
it routes a user’s request to the closest available server (Point of Presence or PoP), which then delivers the cached content, reducing the distance data has to travel.
What are the main benefits of using a CDN?
Faster website loading times, reduced bandwidth costs for the origin server, improved content availability/reliability, and better security (e.g., DDoS protection).
Is a CDN a replacement for my web host (origin server)?
No. A CDN caches and delivers content, but it cannot replace the origin server, which holds the original, complete, and up-to-date version of your website and applications.
What kind of content can a CDN deliver?
Primarily static content (images, CSS, JavaScript, videos) but many modern CDNs also offer solutions for accelerating dynamic content (content that changes per user/request).
Conclusion
The Content Delivery Network is no longer a luxury for just giant corporations; it’s a foundational necessity for any serious website aiming for global reach and high performance. By distributing your content across a vast, intelligent network of edge servers, a CDN radically shortens the data’s journey, slashes server load, and acts as a primary defense against traffic overload and cyber threats. Implementing a CDN is arguably the most impactful single step you can take to instantly turbocharge your website speed, improve user satisfaction, and ensure your digital presence is both fast and resilient.
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
