
If you’ve ever worked with Linux, you’ve probably come across the term systemd. It’s one of the most important parts of modern Linux systems, helping your computer start up, manage services, and handle background tasks. But what exactly is systemd, and how can you use it to manage services easily? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
What is systemd?
systemd is a system and service manager for Linux operating systems. In simple words, it’s responsible for controlling how your Linux system boots up and runs background services (also known as daemons).
Before systemd, older Linux systems used SysVinit, which started processes one by one. This method was slow and harder to manage. systemd replaced it to provide faster boot times, better control, and a modern approach to managing system processes.
Why systemd is Important
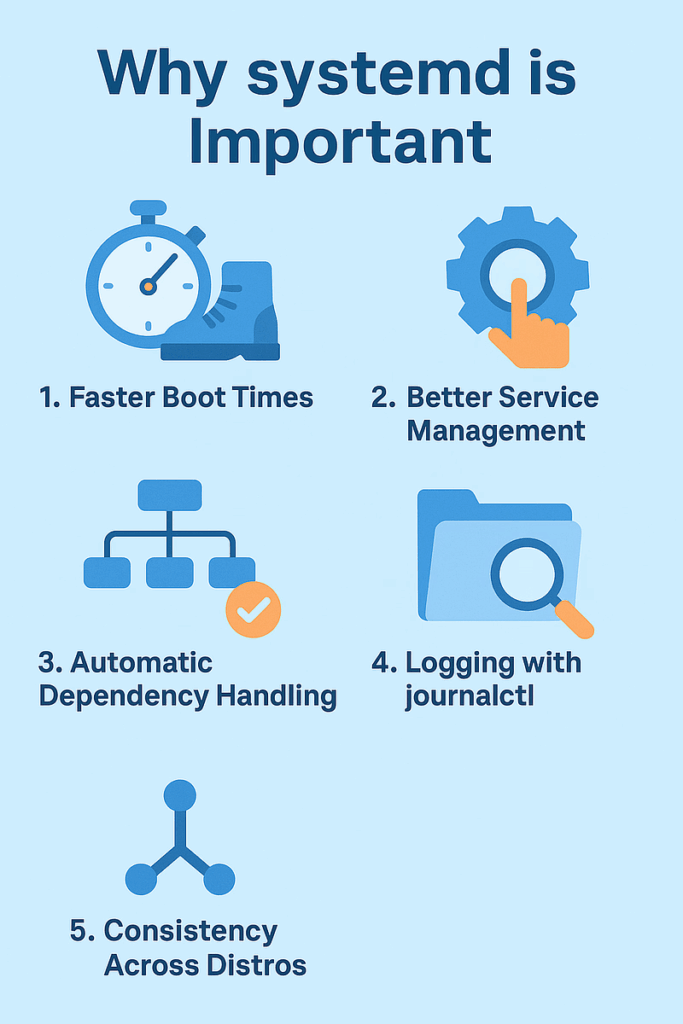
Here’s why systemd is so widely used in modern Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Fedora:
- Faster Boot Times: systemd can start multiple services in parallel, which makes your system boot up faster.
- Better Service Management: It provides tools like systemctl to easily start, stop, or restart services.
- Automatic Dependency Handling: It automatically handles which services need to start before others.
- Logging with journalctl: systemd includes an advanced logging system called journalctl to view and analyze logs.
- Consistency Across Distros: It brings a unified way to manage services across different Linux distributions.
How systemd Works
When you turn on your Linux system, systemd is the first process that runs (PID 1). It then starts all other essential services and background processes according to configuration files called unit files.
Unit files describe how a service should start, stop, or restart. They are usually located in /etc/systemd/system/ or /lib/systemd/system/.
Managing Services with systemd
The main tool you use to manage services is the systemctl command. Here are some of the most common and useful commands:
1. Check the Status of a Service
sudo systemctl status nginxThis command shows whether the service is running, stopped, or failed.
2. Start a Service
sudo systemctl start nginxThis command starts the service immediately.
3. Stop a Service
sudo systemctl stop nginxStops the running service.
4. Restart a Service
sudo systemctl restart nginxRestarts the service—useful after configuration changes.
5. Enable a Service at Boot
sudo systemctl enable nginxThis ensures the service starts automatically when the system boots.
6. Disable a Service
sudo systemctl disable nginxPrevents a service from starting automatically on boot.
7. View All Active Services
sudo systemctl list-units --type=serviceLists all active services currently running on the system.

Using journalctl to View Logs
systemd’s built-in logging tool, journalctl, helps you view logs easily.
View logs for a specific service:
sudo journalctl -u nginxShow real-time logs (like tail -f):
sudo journalctl -u nginx -fThis is helpful for troubleshooting or monitoring services.
Common System Uni Types
| Unit Type | Description |
|---|---|
.service | Defines how a service runs |
.socket | Controls network sockets |
.target | Groups multiple units (like runlevels) |
.mount | Manages mount points |
.timer | Replaces cron jobs for scheduled tasks |
FAQ
What replaced SysVinit in modern Linux?
systemd replaced SysVinit because it’s faster, more reliable, and easier to manage.
How can I check if my Linux system uses systemd?
ps 1
If you see “systemd” in the output, your system uses it.
Is systemd only for servers?
No, it’s used in desktops, laptops, and servers — basically, most modern Linux distributions.
Can I use systemd timers instead of cron jobs?
Yes! systemd timers are more flexible and integrated with system logs.
Where are systemd unit files stored?
Typically in /etc/systemd/system/ (for custom units) and /lib/systemd/system/ (for system ones).
Conclusion
systemd has become the heart of modern Linux systems. It simplifies service management, speeds up boot times, and brings consistency across distributions. Whether you’re managing a server or a desktop, mastering systemd gives you more control and efficiency.
So next time you start, stop, or check a service — remember, systemd is working quietly in the background to keep your Linux system running smoothly.
Would you like me to also create a meta description (160 characters) and focus keywords for this blog for SEO optimization?
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
