
Swap memory in Linux is a reserved storage space on your disk that acts as virtual memory when your system’s RAM is full. Think of it like a backup fuel tank, your computer primarily runs on RAM, but when that’s exhausted, Linux uses swap space to keep things running smoothly instead of freezing.
Swap Memory in Linux: How It Works
Swap comes into action when your system needs more memory than what’s available in RAM. The operating system temporarily moves inactive data from RAM to Swap.
Here’s a simple ASCII overview:
+-----------------+ +----------------+
| RAM | Full | Swap |
| (Fast Memory) | ------> |(Slower Storage)|
+-----------------+ +----------------+RAM is always faster than Swap because RAM is physical memory, while Swap uses storage devices such as SSDs or HDDs.
Tip: If using SSD, Swap is still slower than RAM but much faster than on HDD.
Why Do You Need Swap?
Many beginners wonder, if RAM is faster, why bother with Swap?
Here are some real-world reasons:
- Prevents System Crashes: When RAM is full, Swap ensures the system doesn’t freeze or kill important applications.
- Improves Multitasking: If you run browsers, editors, and heavy apps together, Swap provides breathing room.
- Essential for Low-RAM Devices: Systems with 1–4GB RAM require Swap.
- Useful for Hibernation: Linux hibernation saves RAM data to Swap; requires Swap size ≥ RAM size.
Configure Swap Memory Easily with ServerAvatar (No Commands Needed)
What is ServerAvatar?
ServerAvatar is a platform to simplify the hosting and management of servers and applications. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing PHP and Node.js based web applications on servers.
If you’re using ServerAvatar to host and manage your servers, there’s an even faster and safer way to configure Swap memory, without running a single Linux command.
Manually creating or resizing Swap requires multiple steps, permission settings, and fstab modifications. A small mistake, like an incorrect entry, can cause boot issues. ServerAvatar eliminates this risk by providing a one-click swap management interface and an easy-to-use dashboard.
With ServerAvatar, you can:
- Configure Swap with a few clicks
- Manage server performance visually
- Avoid command-line mistakes
- Monitor RAM, CPU, and Swap in one place
This is useful for everyone, including developers, agencies, and non-Linux experts who just want their server to run smoothly without using terminal commands.
If you prefer GUI-based server management rather than configuring Swap manually, ServerAvatar makes the process effortless and beginner-friendly.
Why Use ServerAvatar to Manage Swap Memory in Linux
With ServerAvatar, you can:
| Feature | ServerAvatar Method | Manual Method |
| Update Swap | One-Click from Dashboard | Requires 8–10 commands |
| Risk of Misconfiguration | Zero (fully automated) | High |
| Time Required | < 10 seconds | 10–15 minutes |
| No Downtime | ✔ Yes | May require reboot if misconfigured |
How to Manage Swap Memory Using ServerAvatar
ServerAvatar gives you full control to update, increase, or decrease Swap Memory:
- Log in to your ServerAvatar account and navigate to the Server Panel by clicking on the server dashboard icon.
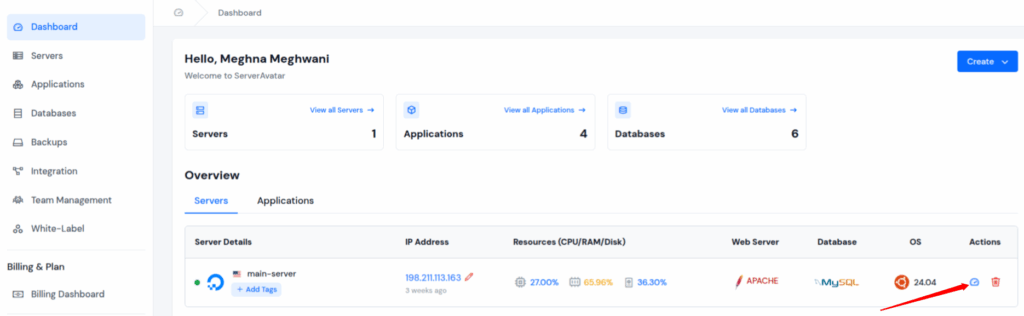
- On the Server Panel, locate the Swap Memory section, and click on the Update Swap button.

- In the pop-up box, review your server’s Current Swap Memory and enter the New Swap Memory value in GB, and click on the Update button to apply changes.
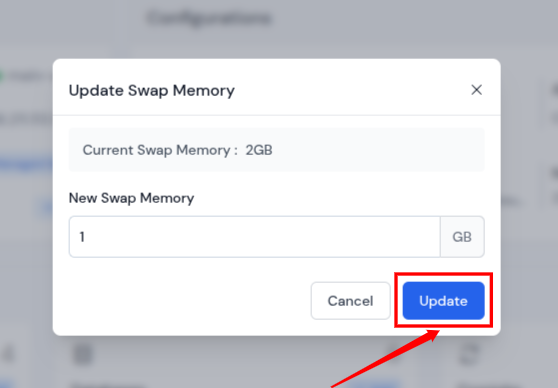
- The changes may take a minute. Once completed, the Swap Memory section will reflect the new size.
That’s it, ServerAvatar will configure everything in the background, including permissions and system configuration.
Example Use Cases
| Use Case | Suggested Swap | Why |
| Low-RAM VPS (1GB–2GB) | 2GB–4GB | Prevents OOM kills and crashes |
| RAM spike due to traffic/load | Increase temporarily | Helps your app survive traffic peaks |
| After upgrading physical RAM | Reduce Swap | Optimizes performance |

Manual Method to Configure Swap Memory in Linux
- Check Current Swap Memory
Before creating Swap, let’s check if Swap already exists using the command below.
swapon --showor
free -h- Expected output example:
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3.8G 2.1G 500M 189M 1.2G 1.3G
Swap: 0B 0B 0BIf Swap: shows 0B, it means no Swap is currently configured
- Create a Swap File (Ubuntu/Debian)
Below is the most common and recommended method to create a Swap.
- Example: Create a 2GB Swap File
sudo fallocate -l 2G /swapfile- If fallocate fails, use:
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=2048- Set the Correct Permissions
Let’s now set the correct permissions for swap using the command below.
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile- Mark It as Swap Space
Mark it as Swap Space by using the command below.
sudo mkswap /swapfile- Enable Swap
Let’s now enable the swap using the command below.
sudo swapon /swapfile- Verify Swap Is Active
Let’s now verify if the swap is active or not.
swapon --showPlease note that only the root user can access it, exactly how it should be.
Helpful Swap Commands for Monitoring
Here are some useful commands to monitor swap usage:
| Command | Description |
free -h | Shows RAM & Swap usage |
| swapon –show | Displays active Swap |
top or htop | Shows memory & swap usage in real time |
| vmstat | Displays system memory statistics |
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Setting Up Swap Memory in Linux
Here are frequent errors beginners make:
- Creating Too Large Swap: If you create 16GB Swap on a system with 2GB RAM, it may slow performance.
- Wrong fstab entry: A typo can make the system fail to boot.
- Forgetting permissions: Swap must only be readable by root.
- Removing or Disabling Swap: If you no longer need Swap, follow these steps.
Conclusion
Swap Memory plays a crucial role in maintaining system stability and performance, especially when your RAM becomes fully utilized. It works as a backup layer that prevents applications from crashing, supports multitasking, and ensures smoother performance for low-RAM systems or high-load environments.
While the manual method gives you complete control over how Swap is configured on Linux, it requires technical knowledge, multiple commands, and careful system configuration to avoid mistakes. This is where ServerAvatar makes a huge difference. With its one-click Swap management feature, you can create, increase, or decrease Swap without touching the terminal, perfect for beginners, developers, agencies, or anyone who wants a hassle-free server management experience.
Whether you prefer the manual approach or a GUI-based solution like ServerAvatar, the key is to allocate the right amount of Swap and configure it properly for the best performance. With the right setup, your server will run more efficiently, stay stable under heavy load, and offer a smoother experience for your applications.
FAQs
1. What is Swap in Linux, and why is it needed?
Swap is virtual memory on your storage device, used when RAM is full. It prevents system crashes and helps with multitasking.
2. Is Swap Memory still needed if I have enough RAM?
Yes. Even with high RAM, Swap is important as a fallback to handle sudden memory spikes, run memory-intensive applications, or enable hibernation on Linux.
3. Can I manage Swap without using terminal commands?
Absolutely. If you’re using ServerAvatar, you can create, update, or remove Swap with one click directly from the dashboard, no Linux commands required.
4. Does enabling Swap require a server reboot?
No. Swap can be enabled or increased in real-time without restarting the server. ServerAvatar also handles this process without downtime.
5. What is the advantage of using ServerAvatar for Swap management?
ServerAvatar automates the entire process with a single click—reducing configuration time, avoiding command-line errors, and making it simple for both technical and non-technical users.
