
Managing a server can feel overwhelming at times, especially when you’re dealing with repetitive tasks, checking logs, tracking resource usage, or maintaining backups. But if you’re comfortable with Linux, even at a basic level, you can use Bash scripts to automate many of these daily chores. Think of Bash scripts as your personal assistants that don’t complain, don’t get tired, and follow your instructions exactly.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the top 10 Bash scripts that every server admin should keep in their toolbox. Each script is simple, practical, and designed to save time while reducing the chances of human error.
1. Bash Scripts for System Resource Monitoring Script
This script gives you an instant snapshot of your server’s overall health by checking CPU load, RAM usage, and disk space. Instead of running multiple commands manually, this single Bash script collects everything in one place, making it easier and faster to understand how your server is performing.
Why it’s useful:
- Instead of typing 3–4 commands separately, you get CPU, memory, and disk details in one clean view.
- Whether you’re troubleshooting or doing routine checks, this script provides instant answers and reduces manual effort.
- You can quickly figure out:
- Is the CPU overloaded?
- Is RAM running out?
- Is the disk about to fill up?
- Useful when applications slow down or crash unexpectedly.
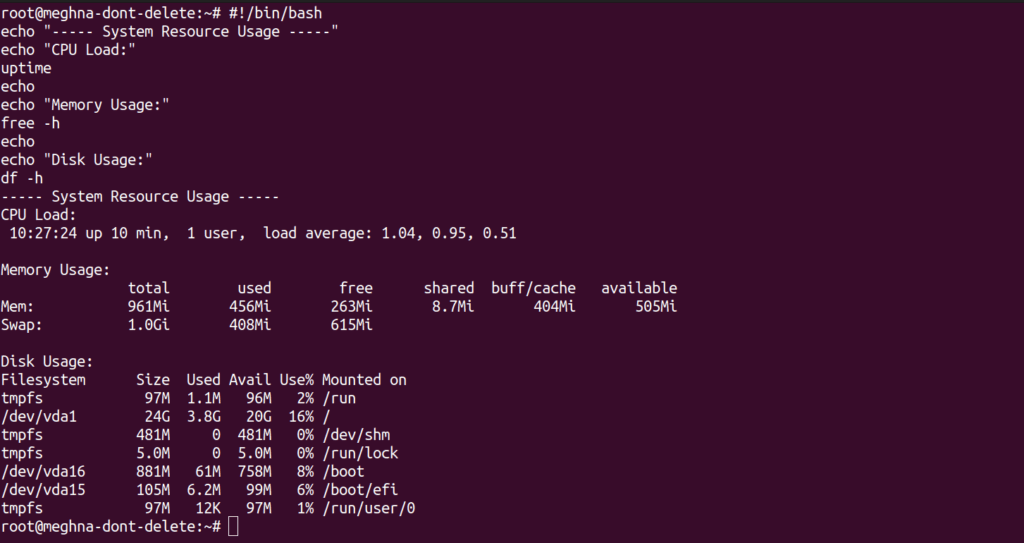
#!/bin/bash
echo "----- System Resource Usage -----"
echo "CPU Load:"
uptime
echo
echo "Memory Usage:"
free -h
echo
echo "Disk Usage:"
df -hOutput:
2. Automatic System Update Script
Keeping your server updated is one of the most important steps in maintaining security and stability. Outdated packages often contain vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit, so regular updates are essential. Instead of running update commands manually every time, this simple Bash script automates the entire process and ensures your server always stays up-to-date.
Why it’s useful:
- Keeps Your Server Secure
- Instead of typing update commands every few days, you just:
- Run the script Or schedule it with cron
- Running multiple update commands manually increases the chance of mistakes.
- This script reduces human error.
- No extra tool or configuration is needed, just a simple Bash script.
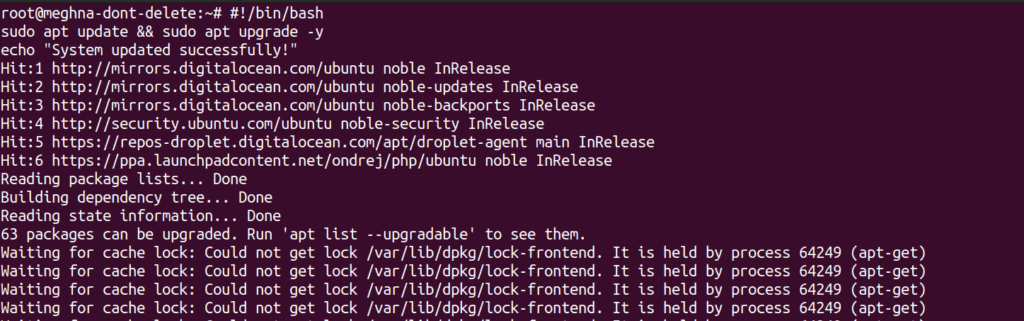
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
echo "System updated successfully!"Output:
3. Bash Scripts for Failed Login Attempt Checker
Brute-force attacks are one of the most common threats faced by Linux servers. Attackers use automated scripts to guess SSH passwords by trying hundreds or thousands of combinations. Monitoring these failed login attempts is crucial because it helps you detect suspicious activity early and take action before your server gets compromised.
This Bash script scans your SSH authentication logs and shows you which IP addresses are repeatedly failing to log in. It gives you a clear view of potential attackers.
Why it’s useful:
- Detects Brute-Force Attacks Quickly
- This script filters the important data and shows it clearly.
- This script helps you understand:
- Attack patterns
- Targeted usernames
- Frequency of attacks
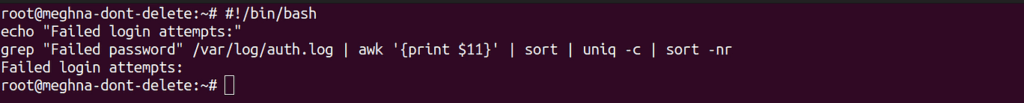
#!/bin/bash
echo "Failed login attempts:"
grep "Failed password" /var/log/auth.log | awk '{print $11}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -nrOutput:
4. Bash Scripts for Disk Space Alert Script
Disk space is one of the most sensitive resources on a server. If your storage gets full, essential services like databases, applications, and even the operating system can crash instantly. Logs stop writing, updates fail, and deployments break. That’s why it’s essential to monitor disk usage and get alerts before things reach a critical point.
This Disk Space Alert Script automatically checks how much space is used on your server and sends an email notification if usage crosses a predefined limit. It’s a simple yet powerful way to prevent server downtime.
Why it’s useful:
- This script notifies you before issues like MySQL crashes, Apache/Nginx failures, broken deployments, or system freezes occur
- This helps keep your server stable and responsive
- The script automatically checks disk usage and notifies you
- The script acts like an early-warning system
#!/bin/bash
THRESHOLD=80
USED=$(df / | grep / | awk '{ print $5 }' | sed 's/%//g')
if [ "$USED" -gt "$THRESHOLD" ]; then
echo "Disk space alert: $USED% used!" | mail -s "Disk Alert" admin@example.com
fi5. Automated Backup Script
Backups are your server’s safety net. If anything goes wrong, accidental file deletions, hacking attempts, system crashes, or corrupted data, a proper backup ensures you can restore everything quickly. This simple Bash script automatically creates a compressed archive of important directories and stores it safely for future use.
Why it’s useful:
- If something goes wrong, hacking, corruption, or accidental deletion, you can quickly restore everything from the backup
- You don’t need to manually create backups; pair this script with a cron job so your server backs up automatically
- There’s no dependency on third-party tools or heavy software.
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup"
SOURCE="/var/www"
FILENAME="backup-$(date +%F).tar.gz"
tar -czvf $BACKUP_DIR/$FILENAME $SOURCE
echo "Backup created at $BACKUP_DIR/$FILENAME"6. Service Status Checker Script
When managing a server, one of the most common tasks is checking whether essential services are running. Services like Nginx, Apache, MySQL, Redis, or SSH must stay active for your applications to work properly. Instead of manually typing systemctl commands every time, this script allows you to check the status of any service in seconds.
You simply pass the service name as an argument, and the script tells you whether it’s currently active.
Why it’s useful:
- Instead of typing, ‘systemctl status nginx’, and scrolling through lots of output, you get a simple one-line answer.
- When you manage multiple services, this script becomes a huge time-saver.
- No need to install anything extra, as long as the system uses systemd, it works perfectly.
#!/bin/bash
SERVICE=$1
systemctl is-active --quiet $SERVICE
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "$SERVICE is running."
else
echo "$SERVICE is not running."
fiUsage Example:
./check_service.sh nginx7. Bash Scripts for Log File Cleaner Script
Log files are essential for debugging and monitoring, but they can grow rapidly and consume a huge amount of disk space, especially on busy servers running web apps, databases, or background processes. If old logs are not managed properly, they can fill up storage and lead to performance issues or even server crashes.
This Log File Cleaner Script automatically removes log files that are older than a certain number of days, helping keep your server clean, healthy, and clutter-free.
Why it’s useful:
- Logs can fill gigabytes of space in days on high-traffic servers. By cleaning old logs automatically, you avoid server crashes, failed deployments, stopped services, and full partitions
- Instead of piling up hundreds of files, your log directory stays clean and manageable.
- No special packages required to run this script
#!/bin/bash
LOG_DIR="/var/log"
DAYS=7
find $LOG_DIR -type f -mtime +$DAYS -exec rm -f {} \;
echo "Old logs cleaned."Output:

8. Network Connectivity Checker
Network issues can break applications, stop deployments, and even disconnect your server from the outside world. Whether you’re troubleshooting slow performance, DNS failures, or connectivity problems, the first step is to check whether your server can reach another host.
This simple Network Connectivity Checker script uses the ping command to test if your server can connect to a specific website or IP address. It’s a quick and reliable way to diagnose network-related issues.
Why it’s useful:
- If your server can’t reach the internet or another machine, this script gives you instant insight
- Many server problems are caused by connectivity issues. This script helps you confirm whether:
- Your app can reach external APIs
- Your server is online
- Internal network connections are working
- The ping command exists on all Linux systems, so no installation is needed
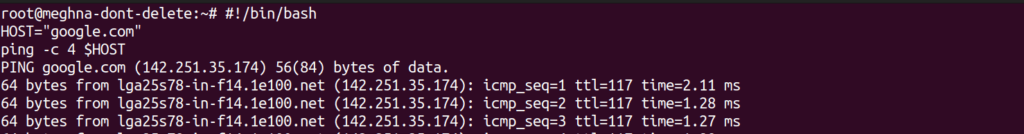
#!/bin/bash
HOST="google.com"
ping -c 4 $HOSTOutput:
9. User Activity Logging Script
On a multi-user server, it’s essential to know who logged in, from where, and at what time. This is especially important for security, auditing, and tracking unauthorized access. Linux provides built-in logs for user activity, and this script makes it easy to view or save that information.
This script uses the last command to show a list of recent logins. You can either display the information directly on the screen or log it into a file for future review.
Why it’s useful:
- This script helps to track active users, suspicious login attempts, unexpected login times, and access patterns
- The script uses the default Linux command, which is available on all systems, so no installation is needed.
- This script helps you track who logged into your server and when.
- It’s an essential tool for security, user monitoring, and server accountability.
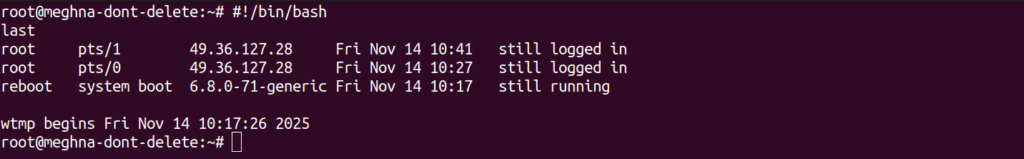
#!/bin/bash
lastOr log it into a file:
#!/bin/bash
last >> /var/log/user_activity.logOutput:
10. Firewall Rule Automation Script
Firewalls are crucial for server security. They control what traffic is allowed in and out of your system. However, managing firewall rules manually, especially on large or multi-service servers, can be confusing and time-consuming.
This simple Firewall Rule Automation Script makes it easy to open ports using UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall), a beginner-friendly firewall tool commonly used on Ubuntu and Debian-based systems. With this script, you can open any port quickly without remembering long commands or making mistakes.
Why it’s useful:
- This script simplifies the process. Perfect for beginners and busy admins.
- Typing wrong commands can break firewall rules and block services. This script reduces the risk.
- This script lets you open any port with one simple command.
- It removes the complexity of UFW and gives you a fast, safe, and reliable way to manage firewall rules on your server.
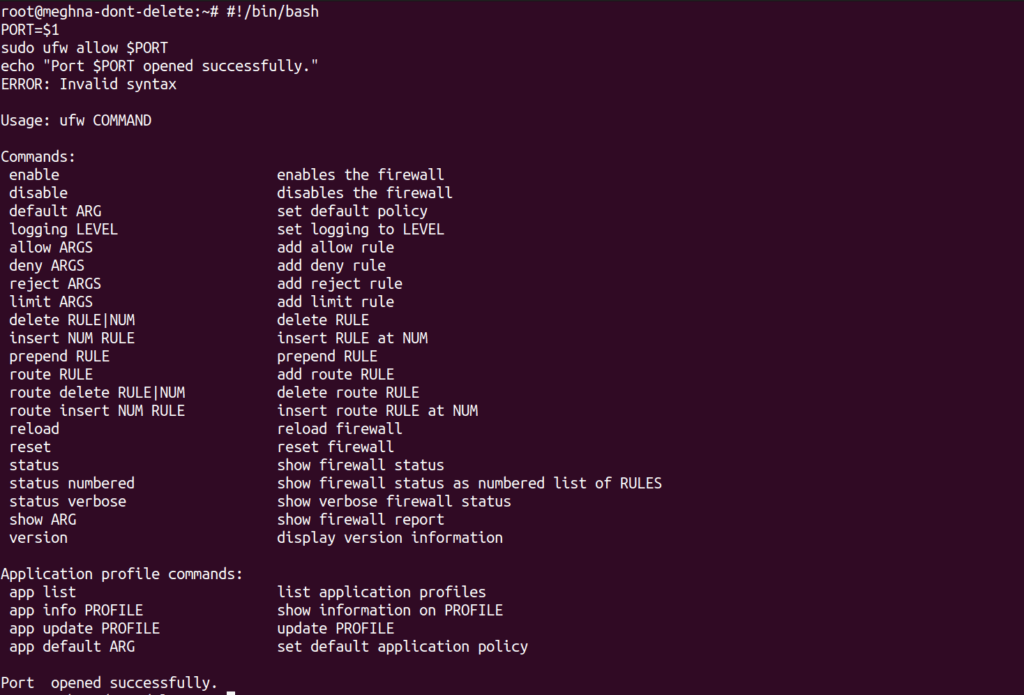
#!/bin/bash
PORT=$1
sudo ufw allow $PORT
echo "Port $PORT opened successfully."Usage:
./open_port.sh 8080Output:
FAQs
1. Do I need advanced Linux knowledge to use these Bash scripts?
Basic familiarity with Linux commands is enough. These scripts are simple, beginner-friendly, and can be copied and used right away.
2. Can I customize these scripts for my own server setup?
Yes, absolutely. All scripts can be modified, for example, changing directories, ports, thresholds, log paths, or backup locations based on your requirements.
3. Are these scripts safe to use on production servers?
Yes, the scripts are safe as long as you review them before executing and adjust values where needed. Always test new scripts on a development or staging environment first.
4. How do I automate these scripts to run daily or weekly?
You can schedule any script using cron jobs.
Example: ‘crontab -e‘
Then add a line like: ‘0 2 * * * /path/to/script.sh‘ – This runs the script daily at 2 AM.
5. Do these scripts work on all Linux distributions?
Most of them work on all Linux distros, but some commands (like apt, ufw, or systemctl) may differ depending on the system. For example: ‘Ubuntu/Debian → uses apt and ufw‘
6. Can I combine multiple scripts into one master script?
Yes. Many admins create a maintenance script that includes resource checks, log cleanup, backup routines, and service monitoring all in one file.
Final Thoughts
Managing a server doesn’t have to be overwhelming or time-consuming. With the right set of Bash scripts, you can automate most routine tasks, reduce human error, and make your server more efficient and secure. Whether you’re checking system resources, detecting failed login attempts, backing up files, or managing firewall rules, these scripts act like reliable assistants that work exactly the way you want, every single time.
The top 10 Bash scripts discussed in this guide are simple yet powerful tools that every server administrator should keep in their toolkit. They help you troubleshoot faster, maintain performance, monitor security, and ensure your server stays healthy with minimal effort.
By incorporating automation into your workflow, you not only save time but also build a more stable and predictable server environment. Start with the basics, customize each script to match your needs, and soon you’ll find your server management tasks becoming smooth, efficient, and stress-free.
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
