
A 403 Forbidden error is a common HTTP status code that indicates an access restriction issue on a website. When this error appears, the server successfully receives the request but refuses to provide the requested resource due to permission or configuration limitations.
This guide explains what a 403 Forbidden error is, why it occurs, and how to fix it step by step using safe and reliable methods. This blog will help website owners, administrators, and developers resolve the issue efficiently without any complexity.
What Is a 403 Forbidden Error?
A 403 Forbidden error means that access to a requested file, folder, or page is denied by the server. The server understands the request but blocks it intentionally due to defined rules or permission settings.
This error typically appears in formats such as:
- 403 Forbidden
- Access Denied
- You do not have permission to access this resource

Unlike a 404 error, which indicates missing content, a 403 error confirms that the resource exists but cannot be accessed.
Difference Between 401, 403, and 404 Errors
These errors are often confused, but each has a different meaning.
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication is required or invalid
- 403 Forbidden: Authentication exists, but access is not allowed
- 404 Not Found: the resource that is requested is not exist
| Error Code | Name | Meaning | Common Cause | How to Fix |
| 401 | Unauthorized | Authentication is required or has failed | Missing, invalid, or expired login credentials | Log in again, provide valid credentials, or refresh the authentication token |
| 403 | Forbidden | Authentication succeeded, but access is not allowed | User does not have permission to access the resource | Request proper permissions or check access control settings |
| 404 | Not Found | The requested resource does not exist | Incorrect URL or deleted/moved resource | Verify the URL, restore the resource, or update broken links |
If you want a detailed explanation of authentication-related access issues, you can read our dedicated guide on the 401 Unauthorized Error
Common Causes of a 403 Forbidden Error
A 403 error can occur for several technical reasons related to permissions, security rules, or server configuration.
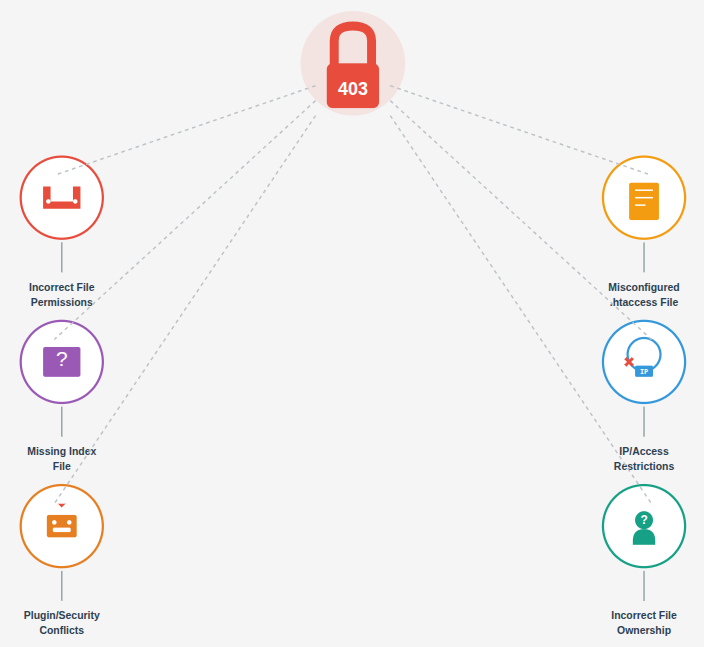
- Incorrect File or Directory Permissions: Servers use permission values to determine who can read, write, or execute files. If these permissions are set incorrectly, access to the resource is denied.
- Misconfigured .htaccess File: The .htaccess file controls access rules at the server level. Invalid directives or restrictive rules inside this file can block access to pages or directories.
- Missing Default Index File: When a directory does not contain a default index file and directory browsing is disabled, the server may return a 403 Forbidden error.
- IP or Access Restrictions: Server firewalls or access control rules may restrict access based on IP addresses, request types, or defined security policies.
- Plugin or Security Rule Conflicts: Certain plugins or security configurations may unintentionally block legitimate requests, resulting in a 403 error.
- Incorrect File Ownership: If files or directories are owned by an incorrect user or group, the web server may not have sufficient permission to serve them.
How to Fix a 403 Forbidden Error
The following solutions address the most common causes of the 403 Forbidden error.
Additionally, Server management platforms like ServerAvatar help website owners and administrators monitor permissions, security rules, and server configurations from a centralized dashboard. This makes it easier to identify and resolve access-related issues such as 403 Forbidden errors while maintaining server stability.
What is ServerAvatar?
ServerAvatar is a platform to simplify the hosting and management of servers and applications. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing PHP and Node.js based web applications on servers.
Various solutions to resolve the most common causes of the 403 Forbidden error.
1. Clear Browser Cache
Browsers store cached data such as images, scripts, cookies, and HTTP responses to improve loading speed and reduce repeated requests to the server. While caching improves performance, it can sometimes cause access-related issues when permission settings or server rules change.
If a browser has stored an older access response, it may continue to display a 403 Forbidden error even after the issue has already been resolved on the server. Clearing the browser cache forces the browser to request fresh data directly from the server instead of relying on stored responses.
Why Clearing Cache Helps Resolve 403 Errors
- Cached permission data may conflict with updated server configurations.
- Browsers can continue using outdated access responses after permission changes.
- Modified access rules or authentication policies may not take effect immediately due to cached data.
- Clearing the cache forces the browser to request the latest version of the resource from the server.
- Stored cookies related to sessions or access validation can interfere with permission checks.
- Removing cached cookies helps reset session data and access-related interactions.
- Clearing cache ensures accurate communication between the browser and the server.
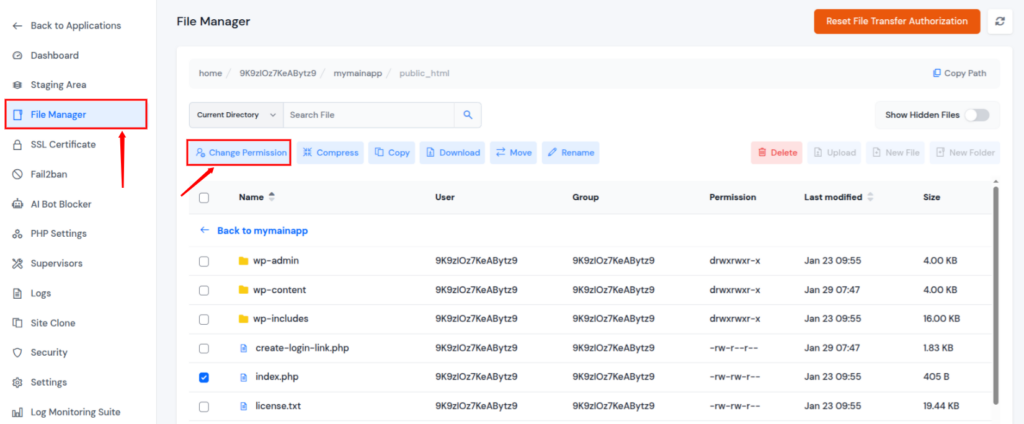
2. Verify File and Folder Permissions
File and folder permissions play a critical role in controlling access to website resources. Incorrect permission values can prevent the web server from reading or executing files, resulting in a 403 Forbidden error. Verifying and correcting these permissions ensures that the server has the required access while maintaining security.
Understanding Permission Values
Permission values define how files and directories can be accessed by the owner, group, and others. Each permission setting determines whether a resource can be read, written, or executed. If these values are misconfigured, the server may block access to the resource even if it exists.
Recommended Permission Settings
To maintain proper access and security, the following permission values are recommended:
- Directories: 755
Allows the owner full access while granting read and execute access to others, enabling directory navigation. - Files: 644
Allows the owner to read and write, while granting read-only access to others, ensuring files can be served correctly.
These permission settings are widely accepted as secure defaults for most web servers.
Why Correct Permissions Matter
When directories lack execute permissions or files lack read permissions, the server cannot access or deliver the requested content. This results in access denial and triggers a 403 Forbidden error. Correct permission values ensure the server can function as intended without exposing sensitive data.
How can ServerAvatar help?
When managing multiple websites or servers, manually verifying file and folder permissions can become time-consuming. ServerAvatar simplifies this process by providing centralized server management, allowing administrators to manage services, configurations, Change File Permission, and access settings efficiently.
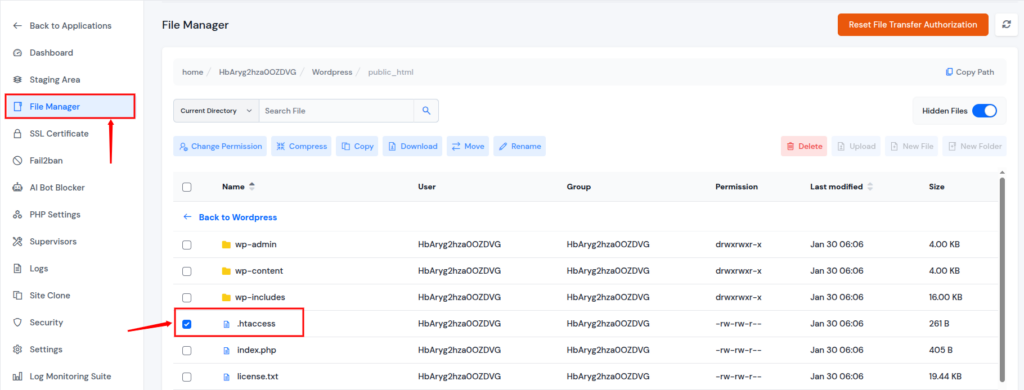
3. Check and Repair the .htaccess File
The .htaccess file is a critical configuration file that controls how the web server handles requests, access rules, redirects, and security settings. An incorrect directive or restrictive rule in this file can block access to resources and trigger a 403 Forbidden error.
Checking and repairing the .htaccess file helps identify misconfigurations that prevent the server from serving content correctly.
How the .htaccess File Affects Access
The .htaccess file can define rules related to authorization, directory access, IP restrictions, and request handling. If these rules are written incorrectly or conflict with server-level settings, the server may deny access even when permissions are correctly configured.
Common issues include invalid syntax, unsupported directives, or access rules that are too restrictive.
Tips for managing .htaccess Files
- Always back up the file before editing
- Make one change at a time and test thoroughly
- Avoid using unsupported or deprecated directives
- Keep the file clean and well-organized
A properly configured .htaccess file ensures correct request handling, prevents unauthorized access issues, and reduces the likelihood of encountering 403 Forbidden errors.
How can ServerAvatar help?
ServerAvatar provides a user-friendly File Manager that makes it easy to access, view, and edit the .htaccess file directly from the dashboard. This allows you to quickly identify misconfigurations, apply changes safely, and restore proper access without needing complex command-line operations.
4. Confirm the Presence of an Index File
Web servers are designed to load a default index file automatically when a directory is accessed. If no index file is present and directory listing is disabled, the server may deny access and return a 403 Forbidden error.
To prevent this issue, it is important to verify that each accessible directory contains a valid index file.
Common Default Index Files
Most web servers recognize the following files as default index files:
- index.php
- index.html
- index.htm
The server will load the first available index file based on its configuration.
Why Missing Index Files Cause 403 Errors
When a directory does not include an index file, the server does not know which file to display. If directory browsing is disabled for security reasons, the server blocks access instead of listing directory contents, resulting in a 403 error.
Tips for Index File Management
- Include an index file in every public directory
- Use consistent naming across the website
- Check index files after migrations or deployments
- Keep index files lightweight and properly structured
Confirming the presence of an index file is a simple yet essential step in resolving and preventing 403 Forbidden errors.
How can ServerAvatar help?
ServerAvatar provides a user-friendly File Manager that makes it easy to access, view, and edit the files directly from the dashboard. This allows you to quickly check if the mentioned files exist.
5. Disable Plugins or Security Modules
Plugins and security modules often control access rules, request filtering, and permission enforcement. If a plugin or security configuration is misconfigured or incompatible, it can block legitimate requests and trigger a 403 Forbidden error.
Temporarily disabling these components helps determine whether the error is caused by a conflict in access rules.
Why Plugins and Security Modules Cause 403 Errors
Access-related plugins and security modules may apply strict filtering rules to protect the website. When these rules are incorrectly defined or conflict with server settings, they can deny access to valid resources. Updates or configuration changes can also alter behavior, leading to unexpected access restrictions.
Tips for Managing Plugins and Security Modules
- Use only necessary and well-maintained plugins
- Keep plugins updated to ensure compatibility
- Review security rules after updates
- Test changes in a controlled environment
Disabling plugins or security modules is an effective troubleshooting step that helps resolve 403 Forbidden errors caused by misconfigured access controls.
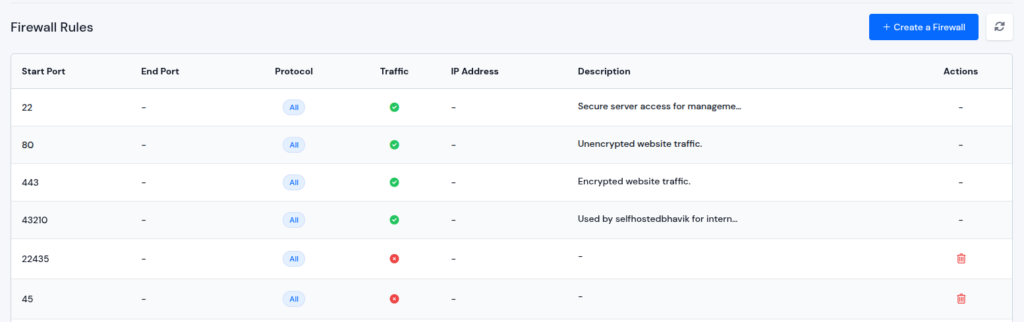
6. Review Firewall and Access Rules
Firewalls and access control rules are designed to protect websites from unauthorized or suspicious requests. However, if these rules are misconfigured or overly restrictive, they can block legitimate access and trigger a 403 Forbidden error.
Reviewing firewall settings and access rules helps identify policies that may be preventing access to public resources.
How Firewall Rules Affect Access
Server-level firewalls and security policies evaluate incoming requests based on predefined conditions such as request type, headers, and access patterns. When a request matches a blocked rule, the server denies access, resulting in a 403 error.
Conflicting rules or outdated policies can continue blocking requests even after other issues have been resolved.
Best Practices for Firewall and Access Management
- Audit firewall rules regularly
- Avoid overly aggressive blocking policies
- Document rule changes for future reference
- Monitor logs to detect repeated access denials
Reviewing firewall and access rules ensures that security measures protect the website without unintentionally blocking valid requests.
How can ServerAvatar help?
Reviewing firewall and access rules can be complex, especially when multiple rules and directories are involved. ServerAvatar allows users to view, create, edit, and delete rules directly from a user-friendly dashboard. This makes it easier to manage firewall, ensure proper access to public resources, and prevent 403 Forbidden errors without needing advanced server commands.
7. Verify File Ownership Settings
File ownership determines which user and group have control over files and directories on a server. Even when permission values are correctly configured, incorrect ownership can prevent the web server from accessing required resources, resulting in a 403 Forbidden error.
Verifying and correcting file ownership ensures that the server has proper authorization to read and serve website files.
How File Ownership Affects Access
Each file and directory on a server is assigned an owner and a group. The web server operates under a specific user account and relies on ownership settings to determine access rights. If files are owned by an unexpected or incorrect user or group, the server may not be able to read or execute them.
Ownership issues often occur after server migrations, restorations, or automated processes that change file attributes.
Tips for Managing File Ownership
- Maintain consistent ownership across the website
- Verify ownership after migrations or backups
- Avoid mixing multiple users for file management
- Document ownership standards for future reference
Verifying file ownership is an essential step in resolving and preventing 403 Forbidden errors caused by access control conflicts.
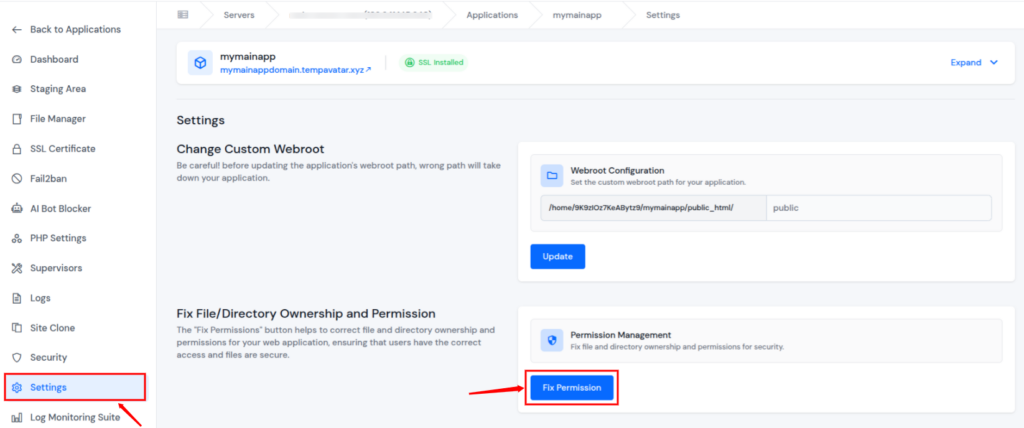
How can ServerAvatar help?
ServerAvatar simplifies ownership and permission management with a “Fix Permissions” button that automatically corrects file ownership and access rights for your applications. This eliminates manual SSH commands and instantly resolves common permission-related issues that can lead to 403 Forbidden errors.
8. Contact ServerAvatar Support
If a 403 Forbidden error persists, the issue may exist at the server level. ServerAvatar support team analyzes server logs, permission conflicts, and security rules to identify the root cause. It provides the exact cause by checking server logs, services, firewall rules, and configuration settings.
Additionally, the ServerAvatar technical experts are available 24/7 to assist you with your issue and resolve your queries and issues.

SEO Impact of a 403 Forbidden Error
A 403 Forbidden error can negatively impact SEO if public pages become inaccessible. Search engines may reduce crawling frequency or remove affected URLs from search results.
Public-facing pages should never return a 403 status unless intentionally restricted.
How to Prevent 403 Forbidden Errors
Preventing 403 Unauthorized errors requires consistent access management, proper configuration, and regular maintenance. Implementing the following best practices helps reduce the risk of access restrictions and ensures stable website availability.
- Maintain Correct File and Directory Permissions: Ensure that files and directories always use recommended permission values. Overly restrictive or overly open permissions can both cause access issues and security risks. Review permissions regularly, especially after deployments or updates.
- Backup Configuration Files Before Changes: Always create backups of important configuration files, including .htaccess, server configuration files, and access control settings. This allows quick recovery if a configuration change results in restricted access.
- Use Access Control Rules Carefully: Apply access restrictions only where necessary. Misconfigured rules, IP restrictions, or authorization directives can unintentionally block legitimate requests. Periodically audit access rules to ensure they align with current requirements.
- Monitor Security and Firewall Policies: Security modules and firewall rules should be reviewed regularly to prevent false positives. Overly aggressive security policies can trigger 403 errors by blocking valid requests. Fine-tune rules to balance protection and accessibility.
- Keep Plugins and Server Software Updated: Outdated plugins or server software may introduce compatibility issues that affect access control. Keeping all components up to date ensures better stability, security, and predictable behavior.
- Verify File Ownership After Server Changes: Server migrations, restorations, or automated processes can alter file ownership. Confirm that ownership settings remain correct so the server retains permission to access required resources.
- Regularly Review Server Logs: Access logs and error logs provide early indicators of permission-related issues. Monitoring these logs helps identify patterns that could lead to 403 Unauthorized errors before they affect site availability.
By following these best practices, websites can significantly reduce the chances of encountering 403 Unauthorized errors and maintain consistent access for users and search engines.
Conclusion
A 403 Forbidden error is a clear signal that access to a resource is being blocked due to permission, ownership, or configuration issues rather than missing content. While the error can seem intimidating at first, it is usually caused by common and fixable factors. By systematically checking website owners and administrators can quickly restore proper access. ServerAvatar further simplifies this process by offering centralized control over permissions, firewall rules, configuration files, and server logs, making it easier to identify and resolve 403 Forbidden errors while maintaining a stable, secure, and SEO-friendly website.
FAQs
1. Is a 403 Forbidden error bad for SEO?
If public pages return a 403 status unintentionally, search engines may stop crawling those URLs or remove them from search results. This can negatively impact rankings and visibility.
2. What file permissions should I use to avoid 403 errors?
Common recommended settings are 755 for directories and 644 for files. These values allow the server to access resources while maintaining security.
3. How can I prevent 403 Forbidden errors in the future?
Maintain proper permissions, back up configuration files before changes, review firewall and security rules regularly, keep plugins updated, verify ownership after server changes, and monitor server logs consistently.
4. Can a 403 Forbidden error be temporary?
A 403 error can occur temporarily due to firewall rules, rate limiting, or security modules that block requests after suspicious activity. Once the restriction is lifted or rules are updated, access is restored.
5. How does ServerAvatar simplify permission management?
ServerAvatar enables users to view and update file and folder permissions from a single interface. This reduces the risk of incorrect permission settings that often lead to 403 Forbidden errors.
6. Is ServerAvatar useful for managing multiple websites with access issues?
ServerAvatar allows users to manage multiple servers and applications from one dashboard, making it easier to manage and monitor servers and applications.
