
If the word Laravel sounds confusing or intimidating, take a deep breath, you are not alone. Many beginners feel the same way when they first hear about it. The good news? Laravel is actually designed to make things easier, not harder. This guide is written especially for beginners who want a clear, friendly, and stress-free explanation.
Think of Laravel like a well-organized notebook. Instead of loose pages everywhere, everything has its own place. You do not need to know advanced technical terms to understand it. We will break down everything easily without rushing. By the end, you will feel confident and comfortable with the basics of Laravel.
What Is Laravel?
Laravel is a PHP framework that helps you build applications in a clean and organized way. Instead of writing everything from scratch, Laravel gives you a ready-made structure.
You can imagine Laravel as a guide that gently holds your hand and says, “Do it this way, it’s simpler.” It removes confusion and replaces it with clarity. Laravel focuses on readable code, so you can easily understand your work even months later.
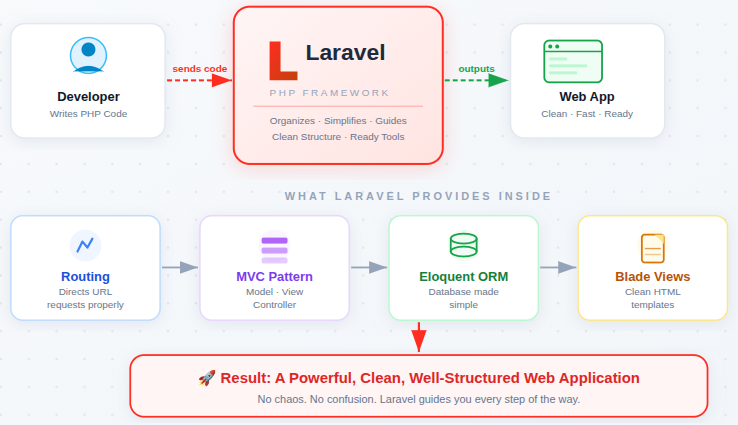
Key Features of Laravel
Laravel provides a powerful set of built-in features that simplify web development. These features work together to reduce manual effort and help developers write clean, organized, and maintainable applications.
Laravel offers:
- MVC architecture: Separates data, logic, and presentation to keep code clean and easy to manage.
- Eloquent ORM: Allows database interaction using simple, readable PHP instead of complex SQL queries.
- Built-in security: Protects applications from common threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
- Clean routing system: Makes it easy to define and understand how URLs connect to application logic.
- Reusable templates: Helps avoid repeating layout code by reusing common page structures.
These features work together to reduce complexity and improve development flow.
Advantages of Laravel
Laravel offers several advantages that make development smoother, especially for beginners. Its thoughtful design helps developers focus more on building features and less on managing repetitive tasks.
Major benefits include:
- Beginner-friendly syntax: Uses simple and expressive code that is easy to read and understand.
- Organized structure: Keeps files and logic neatly arranged, reducing confusion as projects grow.
- Strong community support: Provides access to tutorials, documentation, and solutions from other developers.
- Time-saving tools: Automates common tasks like authentication, validation, and database handling.
Laravel reduces frustration and significantly increases productivity.
Disadvantages of Laravel
Like any development framework, Laravel also has a few limitations. These drawbacks are generally minor and become less noticeable as experience grows.
Common limitations include:
- Slight learning curve at the start: Beginners need time to understand the framework’s structure and flow.
- Performance overhead for very small projects: Lightweight projects may not need a full framework.
- Requires understanding of framework structure: Developers must follow Laravel’s conventions for best results.
These challenges are manageable and improve with regular practice.
Is Laravel a Programming Language?
Laravel is not a programming language. It is a framework built on top of PHP that helps developers write better-organized and more efficient PHP code.
Think of it this way:
- PHP gives you the basic building blocks
- Laravel helps arrange those blocks into a clean and reliable structure
Is Laravel Meant for Frontend or Backend Work?
Laravel is primarily used for backend development. Its main job is to handle logic, manage data, and control how information moves within an application.
Laravel does not focus on visual design or layout by default. Instead, it works behind the scenes, making sure requests are processed correctly and responses are returned smoothly. While it can connect with frontend tools, its strength lies in managing the backend structure.
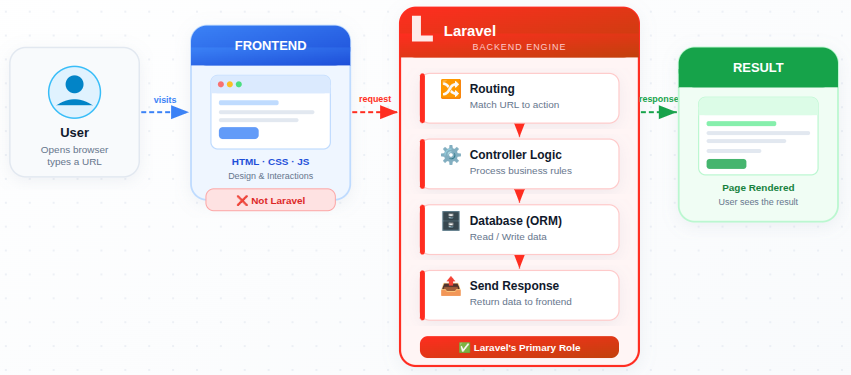
How Laravel Is Not the Same as Plain PHP
Laravel is built using PHP, but it completely changes how PHP projects are structured.
With basic PHP, developers often manage everything manually, which can lead to scattered and hard-to-maintain code. Laravel introduces an organized approach where files follow a clear pattern and responsibilities are separated.
In simple terms, PHP is the language, and Laravel is the system that helps you use that language more efficiently and cleanly.
How Laravel Is Different
Laravel follows modern development practices that keep applications clean and easy to maintain. Instead of mixing logic, layout, and rules in one place, Laravel separates responsibilities clearly.
This separation helps beginners:
- Understand what each file does: Every file has a clear purpose.
- Fix errors faster: Issues are easier to locate and resolve.
- Grow projects without confusion: Applications remain manageable as they scale.
Laravel encourages good habits early, making learning smoother.
Why Laravel Is Beginner-Friendly
Laravel is designed to feel comfortable, even if you are completely new to web development. It does not expect you to know everything from the beginning. Instead, it guides you step by step and encourages good habits early on.
One of the biggest reasons beginners like Laravel is its clear structure. Every file has a purpose, and everything lives in a predictable place. This reduces confusion and makes projects easier to understand as they grow.
Laravel also uses readable and expressive syntax, which means the code often explains itself. Even when you return to your project after a break, it is easy to understand what is happening.
Another major advantage is the strong community and documentation. If you get stuck, chances are someone else already faced the same issue and shared a solution. This support system makes learning less frustrating and more enjoyable.
In short, Laravel is beginner-friendly because it:
- Keeps code clean and organized
- Reduces repetitive work
- Encourages best practices naturally
- Grows with you as your skills improve
Why Do Developers Use Laravel?
Developers use Laravel because it simplifies complex tasks and reduces development effort. It allows teams to build reliable applications faster without sacrificing code quality.
People choose Laravel because it:
- Saves development time: Built-in tools eliminate repetitive manual work.
- Encourages clean structure: Promotes organized and readable code.
- Reduces repetitive work: Common tasks are handled automatically.
- Makes complex tasks simpler: Features like authentication and validation are easy to implement.
Laravel focuses on developer comfort, which appeals to both beginners and experienced developers.
How to Learn Laravel Step by Step
Learning Laravel is most effective when done slowly and in the right order. There is no need to rush or try to understand everything at once.
A comfortable learning path looks like this:
- Understand the folder structure
Learn what folders like routes, app, resources, and database are used for. This builds confidence early. - Learn routing
Understand how URLs connect to actions. Routing is simple and helps you see immediate results. - Practice controllers
Controllers help you organize logic. Learning them early keeps your code clean - Explore views and Blade templates
Learn how pages are displayed and how layouts are reused. - Understand models and Eloquent ORM
This helps you work with data in a clean and readable way. - Learn validation and requests
These features keep your application safe and structured.
Progress may feel slow at times, and that is completely okay. Every small step builds on the previous one. Laravel rewards patience by becoming clearer and more predictable as you move forward.
Remember: slow progress is still progress, and Laravel is designed to support you at every stage of learning.
Understanding Laravel’s Structure
When you open a Laravel project, you may see many folders at first. While this can feel overwhelming, each folder serves a clear and specific role.
Important folders include:
- Routes: Decide how incoming requests are handled.
- Controllers: Contain the logic that processes requests.
- Models: Manage data rules and database interaction.
- Views: Control how content is displayed to users.
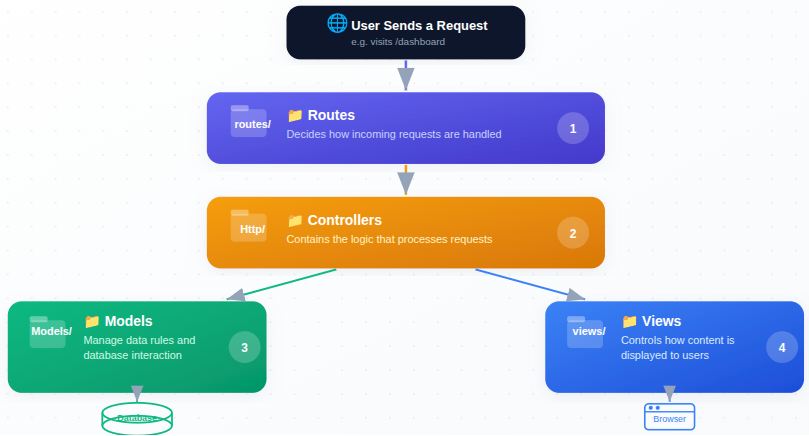
Once you understand this structure, Laravel becomes predictable and easy to follow.
Breaking Down the Laravel Folder Structure
Laravel projects are organized to prevent confusion and improve maintainability. Each folder exists to keep responsibilities separate.
Key folders include:
- routes: Defines application URLs and their actions.
- app: Contains core application logic.
- resources: Stores views and frontend templates.
- database: Manages migrations and database structure.
This organization helps developers quickly find what they need.
The MVC Concept in Laravel
MVC stands for Model, View, and Controller, and it forms the foundation of Laravel.
- Model: Handles data rules and database logic.
- View: Displays information to the user.
- Controller: Connects models and views by processing requests.
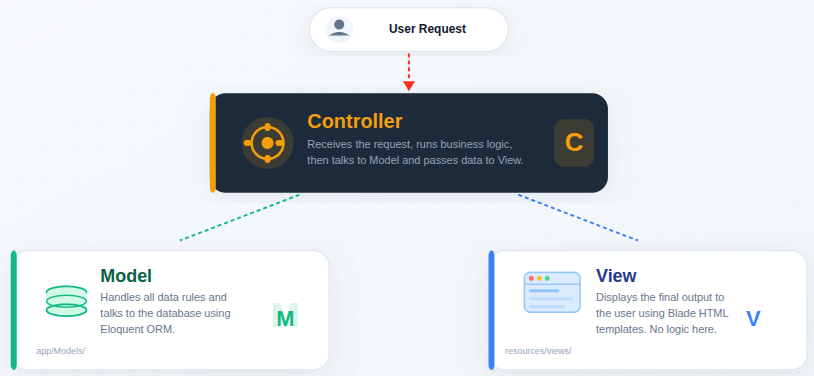
Each part has a single responsibility, keeping applications clean and understandable.
Routing Explained in Simple Terms
Routing tells Laravel what to do when a user visits a specific URL. It acts like a guide that directs requests to the right place.
Routes work like signposts:
- If this path is requested, perform this action.
Laravel routes are clean and readable, which helps beginners understand application flow early.
Routing: How Laravel Understands URLs
Routing tells Laravel what to do when a specific URL is accessed.
A basic route looks like this:
Route::get('/welcome', function () {
return view('welcome');
});Explanation:
- Route::get() defines a route that responds to an HTTP GET request.
- ‘/welcome’ is the URL path users visit in the browser.
- The anonymous function runs when the URL is accessed.
- return view(‘welcome’) tells Laravel to display the welcome.blade.php file.
- This approach is simple and useful for quick or small tasks.
This code tells Laravel:
“Whenever someone opens /welcome, show the welcome.blade.php view.”
Routes act like instructions. They connect URLs to actions and help Laravel know where to send requests.
Controllers and Their Role
Controllers act as decision-makers in a Laravel application. They receive requests, process logic, and return responses.
Benefits of using controllers:
- Cleaner code: Keeps logic out of routes and views.
- Better organization: Centralizes application behavior.
- Easier debugging: Makes issues simpler to track.
Controllers keep applications structured and scalable.
Although logic can be written directly in routes/web.php, this is not recommended for larger or organized applications.
Instead, Laravel encourages separating logic into controllers.
In routes/web.php:
Route::get('/hello', [HelloController::class, 'show']);Explanation:
- This route connects the /hello URL to a controller method.
- HelloController::class points to the controller file.
- ‘show’ is the method that handles the request.
- This keeps routes clean and moves logic into a dedicated file.
- Using controllers improves organization in larger applications.
Inside the controller:
class HelloController extends Controller
{
public function show()
{
return "Hello from Controller!";
}
}Explanation:
- The controller extends Laravel’s base Controller class.
- The show() method runs when the /hello route is accessed.
- It returns a simple text response to the browser.
- Controllers act as decision-makers between routes and views.
- This structure makes applications easier to scale and maintain.
Both approaches work the same way, but using controllers:
- Keeps routes clean
- Makes code easier to manage
- Improves readability
Controllers help keep everything organized and scalable.
Views and Blade Templates
Views control how content appears on the screen. Laravel uses Blade, a simple templating engine, to manage views.
Blade helps you with:
- Reusable layouts: Avoid repeating the same page structure.
- Clean display logic: Keeps presentation separate from logic.
- Simple syntax: Makes templates easy to read and edit.
This makes UI management beginner-friendly.
Models and Data Handling Logic
Models represent how data behaves inside an application. They define rules for storing, retrieving, and managing information.
Models help beginners by providing:
- Less repeated code: Common data logic is reused.
- Clear data rules: Makes behavior predictable.
- Better structure: Keeps database logic centralized.
Models act like a rulebook for application data.
Eloquent ORM: Laravel’s Simple Way to Work With Databases
Eloquent ORM allows developers to interact with databases using clean, readable PHP code instead of complex queries. This makes database operations much easier to understand.
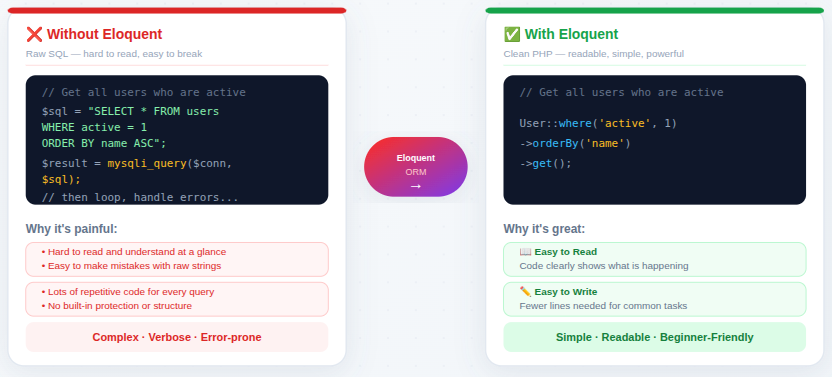
Eloquent makes database operations:
- Easy to read: Code clearly shows what is happening.
- Easy to write: Fewer lines are needed for common tasks.
- Easy to understand: Even beginners can follow the logic.
This simplicity is one of the main reasons beginners love Laravel.
To create a model:
php artisan make:model Student -mExplanation:
- This command creates a new model named Student.
- The -m flag automatically creates a migration file.
- The model represents a database table.
- The migration helps define the table structure.
- Artisan commands save time and reduce manual setup.
A Simple Model Example
class Student extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['name', 'email'];
}Explanation:
- The model extends Laravel’s base Model class.
- $fillable defines which fields can be mass-assigned.
- This protects the database from unwanted data insertion.
- Only name and email can be saved using bulk methods.
- Models keep data logic centralized and clean.
Basic CRUD Operations Using Eloquent
Insert Data
// Insert data
Student::create([
'name' => 'John Doe',
'email' => 'john@example.com'
]);Explanation:
- Creates a new record in the database.
- Uses mass assignment to save data.
- Requires fields to be defined in $fillable.
- Keeps insert operations short and readable.
Fetch All Records
// Fetch all records
$students = Student::all();Explanation:
- Retrieves all records from the students table.
- Returns data as a collection.
- Useful for listing records.
- Simple and easy to understand.
Find Record by ID
// Find by ID
$student = Student::find(1);Explanation:
- Fetches a single record using its primary key.
- Returns null if no record is found.
- Commonly used for detail views.
- Keeps queries minimal and clear.
Update Data
// Update data
$student = Student::find(1);
$student->name = "Updated Name";
$student->save();Explanation:
- Finds a specific record first.
- Updates the required field value.
- Saves the changes to the database.
- Makes updates easy to follow and safe.
Delete Data
// Delete data
Student::destroy(1);Explanation:
- Removes the record with the given ID.
- Performs deletion in a single line.
- Keeps delete logic simple.
- Helps maintain clean database records.
Migrations Explained Clearly
Migrations help track database changes in a structured and safe way. They act like a version history for your database.
Migrations allow you to:
- Apply updates safely: Changes are controlled and predictable.
- Undo changes if needed: Mistakes can be rolled back easily.
- Keep everything consistent: Databases stay in sync across environments.
This reduces fear and increases confidence.

Forms and Requests in Laravel
Laravel manages user input through request objects instead of manual handling. This keeps input processing clean and secure.
Requests help beginners:
- Keep code clean: Input logic stays organized.
- Avoid confusion: Clear separation of concerns.
- Process input safely: Reduces security risks.
Requests act as a filter that keeps everything structured.
Validation Made Easy
Validation ensures users provide correct and safe input. Laravel offers simple rules that automatically check incoming data.
Validation helps beginners by:
- Reducing errors
- Preventing invalid data
- Avoiding long manual checks
Security Basics in Laravel
Laravel includes built-in security features that protect applications quietly in the background.
Key benefits include:
- Safe input handling: Prevents malicious data.
- Protected data flow: Reduces security risks.
- Secure authentication structure: Manages user access safely.
Even beginners benefit from these features without deep security knowledge.
Error Handling and Debugging
Errors are a natural part of learning. Laravel makes debugging easier by showing clear and helpful error messages.
Laravel errors:
- Explain what went wrong: Clear problem descriptions.
- Show where the issue happened: Easy error tracking.
- Help you fix it faster: Saves debugging time.
This clarity reduces frustration and improves learning speed.
Helpful Laravel Tools
Laravel includes tools that reduce manual work and improve confidence.
Helpful tools include:
- Command-line helpers: Speed up common tasks.
- Built-in testing support: Helps ensure code quality.
- Debugging features: Makes troubleshooting easier.
These tools feel like helpful assistants that reduce manual effort and increase confidence.
Beginner-Friendly Laravel Code Examples
Laravel keeps code readable and expressive.
Example of returning a view:
return view('home');Explanation:
- Loads the home.blade.php view file.
- Used to display pages to users.
- Keeps presentation separate from logic.
- Commonly used in controllers.
Example of returning text:
return "Welcome to Laravel";Explanation:
- Sends a plain text response to the browser.
- Useful for testing routes quickly.
- Helps beginners understand response flow.
- Shows Laravel’s simple and expressive syntax.
These examples show how Laravel focuses on clarity. Even without deep knowledge, beginners can understand what the code is doing.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Beginners often struggle due to habits rather than complexity.
Common mistakes include:
- Trying to learn everything at once: Causes overload and confusion.
- Ignoring structure: Leads to messy and hard-to-maintain code.
- Skipping error messages: Misses helpful guidance from Laravel.
When you avoid these mistakes, you can learn Laravel more easily.
Conclusion
Laravel may seem intimidating at first, but as this guide shows, it is actually built to make web development simpler and more structured. From clean routing and MVC architecture to powerful tools like Eloquent ORM and built-in security, Laravel helps beginners write organized, readable, and maintainable code. With its clear folder structure, supportive community, and step-by-step learning approach, Laravel grows with you as your skills improve. If you are starting your journey in backend development, Laravel is a reliable and beginner-friendly framework worth learning.
FAQs
1. Is Laravel good for beginners?
Laravel is very beginner-friendly. It offers a clear project structure, readable syntax, and excellent documentation, which helps new developers learn backend development without feeling overwhelmed.
2. Do I need to learn PHP before learning Laravel?
Having basic knowledge of PHP is important. Laravel is built on PHP, so understanding PHP fundamentals will make learning Laravel much easier.
3. Is Laravel used for frontend or backend development?
Laravel is mainly used for backend development. It handles application logic, database management, routing, and security, but it can work alongside frontend frameworks if needed.
4. Is Laravel suitable for large applications?
Laravel is suitable for both small and large applications. Its MVC architecture and organized structure make it easy to scale projects as they grow.
5. How long does it take to learn Laravel?
The basics of Laravel can be learned in a few weeks with regular practice. Mastery depends on your experience with PHP and how deeply you explore advanced features.
6. Is Laravel still in demand?
Laravel is widely used and remains in high demand. Many companies choose Laravel because it speeds up development and produces clean, maintainable applications.
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
