
Picking the right hosting setup is more than a technical decision, it shapes how reliable, secure, and scalable your website will be over time. When choosing between Managed or Self-Managed Hosting, many businesses and developers feel unsure about which path fits their needs best. With multiple hosting options available today, managed hosting and self-managed hosting remain two widely used approaches, each serving very different needs depending on your technical comfort level and business priorities.
This guide explains hosting from the ground up, highlights the real differences between managed and self-managed environments, and helps you decide which option aligns best with your goals.
What Is Hosting?
Web hosting is service that allow your website to be view on internet. Whether you are running a personal blog, a business website, an online store, or a web application, your website needs a location where all its data can live. This includes files, images, databases, and the code that makes everything work. That location is known as a server.
A server is a high-performance computer that operates continuously, day and night. Its job is to store your website’s data and send it to visitors when they try to access your site. When someone enters your domain name into a web browser, the browser sends a request to the server. The server then processes that request and delivers the website’s content so it can appear on the user’s screen.
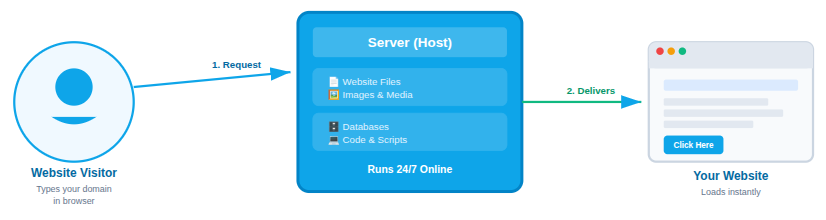
In simple words, hosting is what keeps your website live on the internet and accessible to visitors anytime.
Why Do You Need the Hosting?
A website can’t go live on internet without web hosting. Hosting supplies the technical setup needed to store your website’s content and deliver it safely and efficiently to users anywhere in the world.
Web hosting is important because it:
- Saves all your website files, images, and databases
- Keeps your website available online at all times
- Helps pages load quickly for a better user experience
- Protects your data through security features
- Supports traffic increases as your website grows
Without a hosting service, your website would remain only on your personal computer and would not be visible or accessible to other users online.
How Does the Hosting Work?
When you buy a hosting plan, you are basically leasing storage space and system resources on a server. Your website’s files are placed on that server, and your domain name is linked to it so visitors can find your site online.
When someone types your website’s URL into a browser, the following steps take place:
- The browser identifies the server connected to the domain name
- The server receives and handles the request
- The website’s data is delivered back to the visitor’s browser
This entire exchange happens within moments, making it possible for users to browse and interact with your website smoothly.
Understanding Hosting Responsibilities
Before comparing managed hosting with self-managed hosting, it’s essential to understand what server management actually means. Hosting goes beyond simply renting server space, it involves handling a range of technical tasks that keep a website secure, fast, and reliable.
Server management typically includes:
- Installing and updating the operating system
- Setting up and configuring web servers such as Apache or Nginx
- Managing databases and related services
- Implementing security measures, including firewalls and system hardening
- Creating and maintaining regular backups
- Optimizing server performance for speed and stability
- Monitoring uptime and overall server health
- Identifying and resolving errors or downtime issues
The main difference between managed and self-managed hosting comes down to responsibility, whether these tasks are taken care of by you or handled by the hosting provider.
Different Types of Hosting
There are several types of web hosting available, each suited to different website requirements and technical experience levels:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites operate on a single server and share its resources
- VPS Hosting: A virtual private server that provides dedicated resources within a shared environment
- Cloud Hosting: Websites are hosted across a network of connected servers for better reliability
- Dedicated Hosting: One entire server is assigned to a single user or website
- Managed Hosting: The hosting provider takes care of server setup, maintenance, and management
- Self-Managed Hosting: The user has full control and is responsible for managing the server
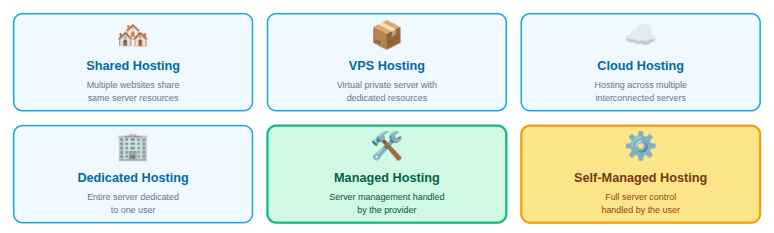
Among these options, managed and self-managed hosting stand out as the most significant choices, especially when it comes to balancing control, responsibility, and overall ease of use.
How Hosting Impacts Your Website’s Success
The performance for website is tied to quality of hosting. Low-quality hosting can cause slow page loads, frequent outages, and increased security risks. In contrast, dependable hosting enhances user experience, supports better search engine visibility, and builds trust in your brand.
Your hosting decision impacts several key areas:
- Website speed and performance: Quality hosting ensures fast loading times and smooth operation for visitors.
- Security and data protection: A reliable host helps safeguard your site against malware, cyberattacks, and data loss.
- Uptime and availability: Good hosting keeps your website online consistently without unexpected interruptions.
- Scalability for future growth: The right hosting solution makes it easy to manage higher traffic and growing resource needs.
- Overall user experience: Stable and responsive hosting creates a positive experience that encourages users to return.
For these reasons, understanding web hosting is an essential first step before choosing between managed and self-managed hosting solutions.
What Is Managed Hosting?
Managed hosting is a type of service where the hosting provider handles the majority of technical tasks on your behalf. This typically includes server configuration, security management, software updates, performance monitoring, regular backups, and, in many cases, issue resolution.
Simply put, managed hosting allows you to concentrate on building and running your website while experienced professionals take care of the server operations.
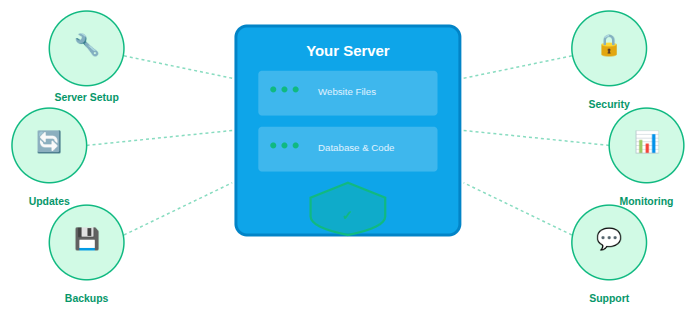
Key Benefits of Managed Hosting
Managed hosting usually comes with a comprehensive set of services included in a single plan. These features are designed to ensure reliability, strong security, and worry-free server management.
Common managed hosting features include:
- Automatic server setup and initial configuration
- Ongoing operating system and software updates
- Integrated security tools and malware protection
- Scheduled backups with easy restore options
- Continuous performance monitoring and optimization
- Access to expert technical support
Because of these built-in services, managed hosting is particularly well suited for non-technical users, startups, and businesses that are scaling their online presence.
Pros of Managed Hosting
Managed hosting is ideal for users who want a hassle-free and reliable website experience. The main benefit is that the hosting provider takes care of all server management tasks, including security, updates, and performance optimization.
The key advantages of managed hosting include:
- No need for advanced technical skills or server management knowledge
- Expert handling of server setup, updates, and ongoing maintenance
- Enhanced security with firewalls, malware scanning, and regular backups
- Improved uptime and continuous performance monitoring
- Direct access to professional technical support when needed
Cons of Managed Hosting
The primary drawback of managed hosting is cost. Because the provider handles most of the technical responsibilities, managed plans are generally more expensive than self-managed alternatives. Another limitation is that you may have less control over certain server settings, and some advanced configurations or custom software installations might not be possible.
Other common downsides include:
- Higher monthly or annual hosting fees
- Limited ability to customize server-level settings
- Reduced control over software and configurations
- Reliance on the hosting provider’s policies and support
Who Should Consider Managed Hosting?
Managed hosting works best for:
- Small businesses that don’t have a dedicated IT team
- Bloggers and content creators who want to focus on content, not servers
- E-commerce websites that prioritize sales over technical management
- Agencies managing multiple client websites
What Is Self-Managed Hosting?
Self-managed hosting is exactly what it sounds like: you manage everything on the server yourself. You choose the operating system, install software, handle security, and optimize performance. With self-managed hosting, you are in control of the entire server environment.
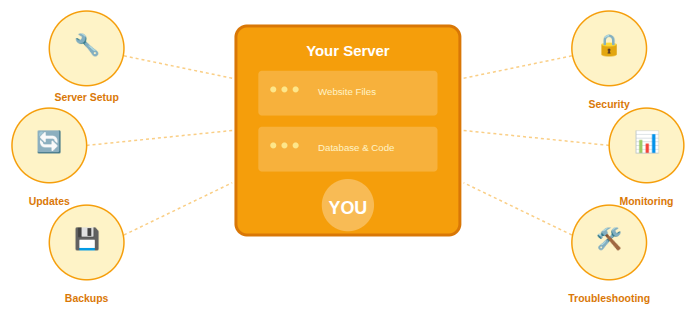
Key Benefits of Self-Managed Hosting
Self-managed hosting provides raw access to your server without additional management services. While this gives you freedom, it also means more responsibility.
- Full root or administrative access
- Freedom to install any software or stack
- Custom server configuration
- Manual updates and maintenance
- Self-managed security and backups
This model is best suited for users who are comfortable working with servers.
Pros of Self-Managed Hosting
Self-managed hosting is ideal for users who want complete control over their server. You decide how the server is configured, which software is installed, and how security is handled.
Key advantages include:
- Full control over the server environment
- Freedom to install and customize any software
- Lower hosting costs compared to managed plans
- Ideal for developers and advanced users
- Better suited for custom or experimental setups
Cons of Self-Managed Hosting
The biggest challenge with self-managed hosting is responsibility. You are fully accountable for server security, updates, performance optimization, and troubleshooting.
Common drawbacks include:
- Requires strong technical and server management knowledge
- No built-in support for server-level issues
- Higher risk of security vulnerabilities if not maintained properly
- Time-consuming maintenance and monitoring
- Performance depends entirely on your configuration skills
Who Should Consider Self-Managed Hosting?
Self-managed hosting works well for:
- Developers and tech-savvy users
- Businesses with internal IT teams
- Projects requiring custom server configurations
- People who want complete control over their environment
Managed vs. Self-Managed Hosting
To help you decide, let’s compare the two across key decision areas:
1. Ease of Use
- Managed Hosting: Extremely user-friendly. Set up is fast, and most technical tasks are handled for you.
- Self-Managed Hosting: Requires technical knowledge. You are responsible for everything.
2. Control and Customization
- Managed: Limited control. You get what the provider supports.
- Self-Managed: Full control over software, configurations, and environment.
3. Security
- Managed: Built-in firewalls, monitoring, and proactive patches.
- Self-Managed: Security is up to you. You must install and maintain protections.
4. Cost
- Managed: Higher monthly cost due to included services.
- Self-Managed: Lower cost, but remember, it requires your time and effort.
5. Performance & Stability
Both can be fast, but:
- Managed: Providers often optimize performance and caching.
- Self-Managed: Performance depends on your server tuning.
6. Technical Support
- Managed: Dedicated support team included.
- Self-Managed: No formal support, you rely on your own skills or community help.
How ServerAvatar Simplifies Managed and Self-Managed Hosting
What is ServerAvatar?
ServerAvatar is a platform to simplify the hosting and management of servers and applications. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing PHP and Node.js based web applications on servers.
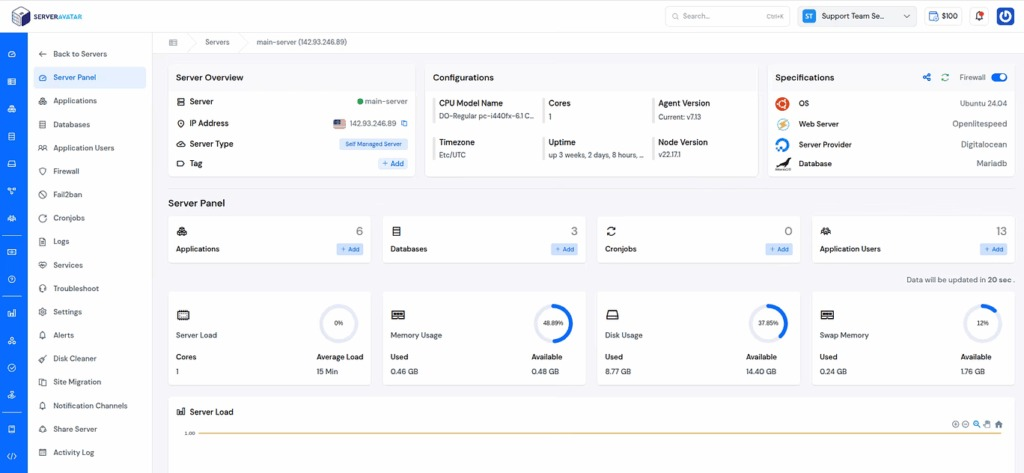
ServerAvatar is designed to make cloud hosting and management simpler, faster, and more reliable. Unlike traditional hosting providers, ServerAvatar gives users the flexibility to choose between Managed Servers and Self-Managed Servers. ServerAvatar offers both options within a single platform.
Managed Servers with ServerAvatar
ServerAvatar’s Managed Server option is ideal for users who want the benefits of cloud hosting without dealing with the cloud provider’s account. With managed servers, ServerAvatar handles the entire server lifecycle, from provisioning to ongoing maintenance, so you can focus on your website or business.
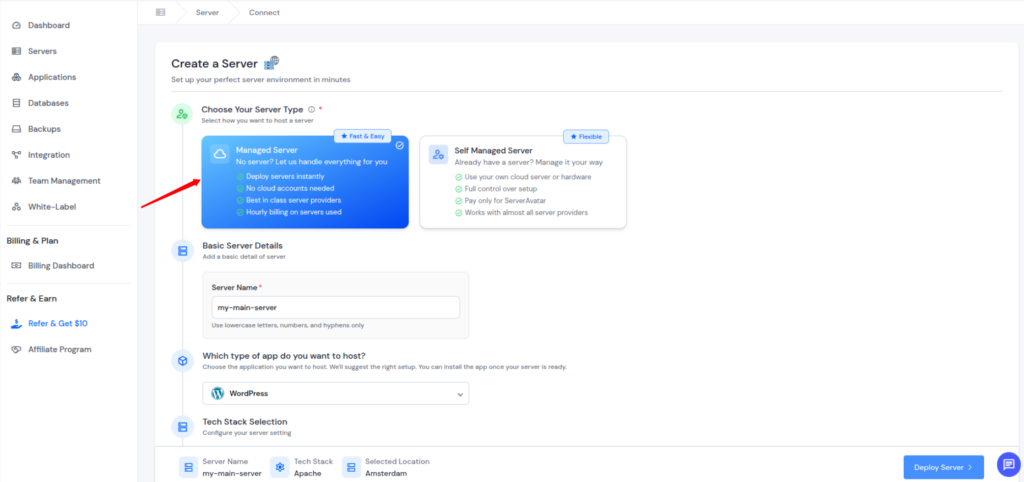
These servers are provisioned and maintained directly by ServerAvatar on trusted infrastructure. You don’t need to create your own cloud provider account.
What ServerAvatar Manages for You
With managed servers, ServerAvatar takes care of:
- Server provisioning and setup
- Operating system and security updates
- Web server and stack configuration
- Performance optimization
- Monitoring and stability
- Core server maintenance
This approach removes the complexity typically associated with cloud hosting while still delivering high performance and reliability.
Who Should Use ServerAvatar Managed Servers
Managed servers are best suited for:
- Businesses without a dedicated DevOps team
- Agencies managing multiple client websites
- Bloggers and content creators
- E-commerce stores that need stability and security
- Anyone who prefers a hands-off hosting experience
You can get more details about Managed Server by navigating to this link: https://serveravatar.com/docs/managed-server/introduction/
Self-Managed Servers with ServerAvatar
For users who want full control over their infrastructure, ServerAvatar also offers Self-Managed Servers. This option allows you to connect your own cloud server from any cloud provider and manage it through the ServerAvatar dashboard.
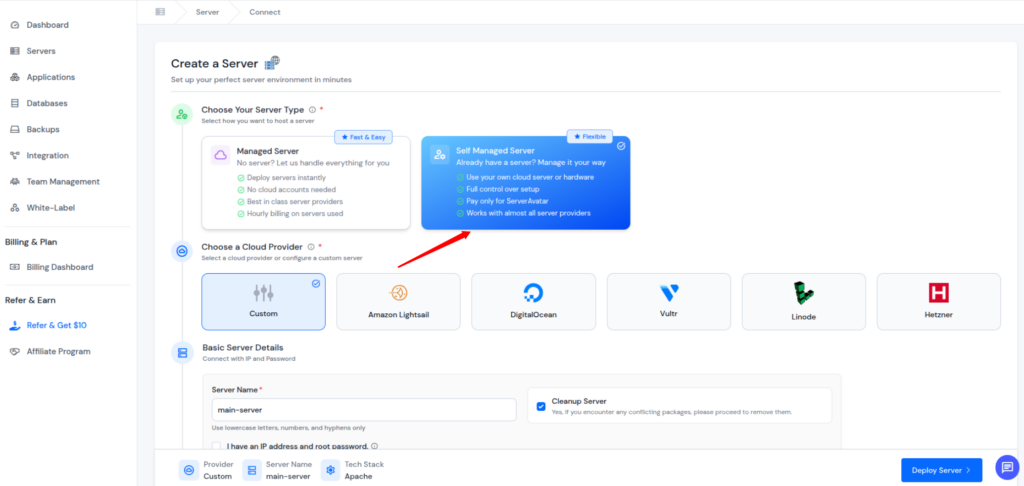
You retain full ownership and control of your server while ServerAvatar provides a clean interface and powerful tools to simplify server management.
Supported Cloud Providers to Integrate
ServerAvatar supports integration of popular cloud provider accounts to create self-managed servers from major cloud platforms, including:
- Amazon Lightsail
- DigitalOcean
- Vultr
- Linode
- Hetzner
You can integrate your preferred provider, create a server, and connect it to ServerAvatar using guided installation steps. Additionally, you can also create a server from any cloud provider using the Direct Method.
What You Control in Self-Managed Servers
With self-managed servers, you are responsible for:
- Connect server from any cloud provider
- Integrate a popular cloud provider account
- Connect the server with or without an IP address and a root password
ServerAvatar acts as a management layer, helping you deploy and manage applications efficiently without removing control.
Who Should Use ServerAvatar Self-Managed Servers
Self-managed servers are ideal for:
- Developers and system administrators
- Teams with technical expertise
- Custom or high-performance applications
- Projects requiring specific server configurations
You can get more details about the Self Managed Server by navigating to this link: https://serveravatar.com/docs/server-management/installation/direct-method/
Managed vs Self-Managed Hosting with ServerAvatar: Choosing the Right Option
One of the biggest advantages of using ServerAvatar is that you don’t have to commit to a single hosting approach. You can choose managed servers for simplicity or self-managed servers for flexibility, based on your project’s needs.
Choose ServerAvatar Managed Servers if:
- You want minimal server responsibilities
- Security and stability are top priorities
- You prefer expert-managed infrastructure
- You want to save time and operational effort
Choose ServerAvatar Self-Managed Servers if:
- You want full control over your cloud server
- You already use a preferred cloud provider
- You have the technical expertise to create servers
Both options give you access to ServerAvatar’s application management tools, clean dashboard, and scalable architecture.
Why ServerAvatar Is a Smart Choice for Both Hosting Models
Unlike traditional hosting platforms that force users into a single approach, ServerAvatar is built for flexibility. It supports both beginners and advanced users without compromising performance or control.
By offering managed and self-managed servers under one platform, ServerAvatar allows you to:
- Start simple and scale technically over time
- Manage multiple servers from one dashboard
- Reduce dependency on multiple tools
- Maintain consistency across projects
This makes ServerAvatar a practical long-term solution for individuals, agencies, and growing businesses.

Detailed Use Cases to Help You Decide
To make this even clearer, here are some real-world scenarios:
🔹 Use Case: Small Business Owner
If you run a business and want to focus on customers, sales, and products, not servers, managed hosting is a clear choice. You benefit from expert support, automatic backups, and superior security.
Recommended: Managed Hosting
🔹 Use Case: Developer or Freelancer
If you love tinkering with servers, want full control, and can troubleshoot issues, self-managed hosting gives you freedom and flexibility.
Recommended: Self-Managed Hosting
🔹 Use Case: Tech Startup
Startups with an in-house team may prefer self-managed hosting initially to control costs and customize the environment. But if your team is small and busy, managed hosting might reduce workload.
Recommended: Depends on Team Resources
How to Choose: A Quick Checklist
Ask yourself:
- Do I want to focus on my business rather than servers?
- Do I have technical expertise or a team to manage hosting?
- Is budget my most important factor?
- How critical is uptime and security for my site?
- Do I need advanced customization?
If most answers point to simplicity, security, and support >> Managed Hosting
If most answers point to control, flexibility, and cost savings >> Self-Managed Hosting
Which Hosting Option Is Best for You?
Your decision should be based on your technical skills, business goals, and available resources.
Choose managed hosting if you want:
- Simplicity and peace of mind
- Strong security and reliability
- Professional support
- More time to focus on growth
Choose self-managed hosting if you want:
- Full control and customization
- Lower upfront costs
- Advanced server-level access
- A hands-on technical experience
Conclusion
Choosing between managed and self-managed hosting depends on how much control, responsibility, and technical involvement you want in running your website. Managed hosting is ideal for users who prioritize simplicity, security, and reliability, allowing them to focus on growth while experts handle server management. Self-managed hosting, on the other hand, offers full control and flexibility for developers and technical teams who are comfortable managing servers themselves.
With ServerAvatar, you don’t have to compromise; its platform supports both managed and self-managed servers, giving you the freedom to choose the right approach for each project and scale confidently as your needs evolve.
FAQs
1. Is managed hosting better than self-managed hosting?
Managed hosting is not necessarily better, it is simply more convenient. It is ideal for users who want ease of use, security, and support. Self-managed hosting is better for users who want full control, customization, and lower costs and have the technical expertise to manage servers.
2. Can beginners use self-managed hosting?
Beginners can use self-managed hosting, but it is not recommended unless they are willing to learn server management. Without proper knowledge, self-managed hosting can lead to security risks, downtime, and performance issues.
3. Does ServerAvatar support both managed and self-managed hosting?
Yes, ServerAvatar offers both Managed Servers and Self-Managed Servers, allowing users to choose the level of control and responsibility that best suits their needs, all from a single platform.
4. Do I need a cloud provider account for ServerAvatar Managed Servers?
No, with ServerAvatar Managed Servers, you do not need to create or manage a cloud provider account. ServerAvatar handles server provisioning and maintenance for you.
5. Which cloud providers are supported for ServerAvatar Self-Managed Servers?
ServerAvatar supports self-managed servers from popular cloud providers such as Amazon Lightsail, DigitalOcean, Vultr, Linode, and Hetzner. You can also connect servers from any other providers using the Direct Method.
