
Have you ever wondered why your favorite website sometimes takes ages to load, or why your video call gets choppy all of a sudden? If this sounds familiar, you’re not alone. The internet’s invisible highways are filled with twists, turns, and occasional roadblocks. The good news? There’s a tool designed to help uncover where things go wrong. Meet the traceroute command – your personal detective for digital traffic jams.
In this article, you’ll discover what the traceroute command does, how it works, how to use it, and why it’s so important for diagnosing those mysterious network slowdowns. We’ll keep it simple, skip the jargon, and sprinkle in analogies and examples you’ll actually relate to.
What is the Traceroute Command?
Imagine your data is like a package being mailed to a friend across the country. On its way, it passes through many post offices. If the package is late, wouldn’t it be nice to see exactly which post office is the hold-up? That’s exactly what the traceroute command does for your internet traffic.
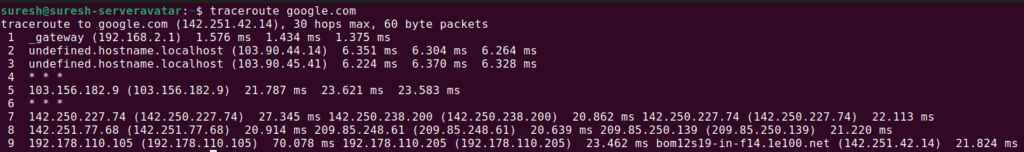
The traceroute command is a simple tool that shows every “stop” (or router) your data hits on its way to its final destination. It also shows how long it takes to get through each stop. In essence, traceroute is a network map and stopwatch in one.
How Does Traceroute Command Work?
When you use the traceroute command, it sends out test packets with a time-to-live (TTL) number attached. Each time the packet passes through a router, the TTL drops by one. When it hits zero, the router says, “That’s as far as I’ll take you,” and sends back a message. This lets traceroute know how long the trip took up to that point.
Traceroute keeps sending more packets, upping the TTL each time, until the packets reach their destination or a set maximum number of hops. For each “hop,” it tells you which device was hit and how long it waited there.
It’s like tracking a relay race, seeing which runner slows things down.
Traceroute vs Ping: What’s the Real Difference?
You might have heard of ping – another simple network tool. But here’s an easy way to separate them:
- Ping: Like asking, “Are you there?” and getting a yes or no (plus response time).
- Traceroute: Like asking, “How did you get here, and where did you stop along the way?”
If you only care whether a device is reachable, ping is enough. But if you want to know where the journey goes wrong, traceroute is your friend.
Running Your First Traceroute Command
On Windows:
Open Command Prompt and type:
tracert example.comOn Linux or MacOS:
Open Terminal and type:
traceroute example.comReplace “example.com” with the website or IP you want to test.
Within seconds, you’ll see a list of hops – every router your packet touches, along with three response times for each. The closer the numbers are to zero, the faster that link is!
Understanding Traceroute Command Output
If your results look confusing, relax – let’s decode them step-by-step.
Each line represents a different hop (router). You’ll see:
- Hop number: The order in the journey.
- IP Address/Host: Identity of each router.
- Three times (in ms): How long (in milliseconds) each attempt took.
If you see asterisks (*), it means there was no reply – lots of asterisks could mean a firewall or a downed router.
A steadily rising time is normal (traffic usually slows down as distance increases). But if one hop takes much, much longer, you may have found the bottleneck!
Common Problems Traceroute Command Reveals
- Sudden, sharp jumps in response time: Usually, this is the troubled link.
- Several hops showing ““:* The router may be blocking traceroute, or it’s down.
- Repeating IP addresses in consecutive hops: That’s a routing loop – a problem in the network’s directions.
- Doesn’t reach the destination: There may be a big outage between you and the site.
Advanced Traceroute Command Tricks
Want to look like a pro? Here are a few cool extras:
- Change the number of queries per hop (for better accuracy):
traceroute -q 5 example.com - Set a longer wait time (helpful for slow or distant links):
traceroute -w 10 example.com - Try different protocols (handy when firewalls block standard traceroute):
- ICMP:
traceroute -I example.com - TCP:
traceroute -T example.com
- ICMP:
- Limit hop count:
traceroute -m 15 example.com
On Windows, check tracert /? for available options.
Real-World Troubleshooting Scenarios
Let’s imagine a few situations where the traceroute command saves the day:
Scenario 1: The Laggy Video Call
You’re in the middle of an online meeting and suddenly video lags. You run a traceroute to the meeting server and spot a big delay at your local ISP’s router. Now you know: the bottleneck is close to home – not your software or hardware.
Scenario 2: The Global Website Slowdown
Your New York users say your site is lightning fast, but folks in Japan complain it’s slow. A traceroute reveals smooth hops in the US but huge time jumps across the Pacific. The solution? Consider hosting a mirror server in Asia – or read more about how server location affects latency.
Scenario 3: The Mystery Firewall
Everything works fine except connection to one service. Traceroute hits a brick wall – ”***” – at your company’s firewall. A quick call to IT solves the mystery!
Scenario 4: The Geographic Distance Problem
If your users are spread across continents and latency varies wildly, a trace shows you the clear connection between distance and speed. When traceroute reveals consistently high latency due to server distance, the solution often involves strategic server placement. Understanding how server location affects latency becomes crucial for optimizing user experience across different geographical regions.
How Server Location Affects Latency
Think about it: if you order pizza from the shop next door, it gets to you fast. If you order from across the country, you’ll be waiting a lot longer. The same is true for web servers.
Data, just like pizza, must travel. The farther away the server is from the user, the more time (latency) it takes. For instance, someone in India reaching a US server might have 250ms latency, but only 30ms if the server is in Mumbai.
Sometimes, even with nearby servers, things like DNS and poor routing can slow down data – another reason why traceroute is so useful!
How to Choose the Right Server Location
Want a faster site? Host your server near your main audience! Use tools and dashboards (like ServerAvatar) that let you pick server regions based on your traffic’s geography.
Consider using a Content Delivery Network (CDN), which caches your site on multiple servers worldwide, delivering your content from the location closest to each visitor.
Pro-tip: Always review your analytics for your users’ locations before choosing a server spot.

Traceroute Command Limitations
Traceroute is powerful, but it’s not magic:
- Some routers block or ignore traceroute packets, showing false “timeouts.”
- Modern networks may use load balancing, meaning routes and results can change often.
- Real user data sometimes takes different paths than diagnostic traces.
- Firewalls can block traceroute results even if real traffic flows fine.
Tips for Using Traceroute Wisely
- Establish a baseline: Run regular traceroutes when all is well, so you know what “normal” looks like.
- Test from many locations: The more points of view, the clearer the network picture.
- Combine with ping: Ping for basic availability, traceroute for path diagnosis.
- Keep logs: Track issues, output, dates, and times. Patterns often emerge!
- Be respectful: Don’t spam traceroute tests. They do generate a bit of extra internet traffic.
Combining Traceroute Command with Other Tools
Traceroute is just one tool in your kit. Pair it with:
- Ping: Quick checks on reachability.
- MTR: Combines ping and traceroute for continuous monitoring.
- PathPing (Windows): Extended version giving stats for each hop.
- Network Monitors: Enterprise tools (like Nagios) integrate traceroute for ongoing alerts.
If you want to dive deep into how packets travel and what really happens at each hop, Cisco’s documentation is an excellent technical reference.
Security and Ethical Precautions
- Only test networks you own or are permitted to troubleshoot.
- Never use traceroute (or any diagnostic tool) to scan or probe someone else’s network without explicit permission.
- Be aware that results reveal your network’s structure. Routers may intentionally block responses to hide this information.
Conclusion & Next Steps
The traceroute command is like a traffic report for your data – showing you where things slow down, get stuck, or stop completely. Whether you’re an everyday user, a small business owner, or a web developer, knowing how to use traceroute puts you in control of your digital experience.
Next time your video call freezes or a website drags, you can take matters into your own hands. Diagnose the issue. See where the slowdown is. And take steps – like moving your server, using a CDN, or optimizing your network – to ensure your online world runs at the speed of now.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between tracert and traceroute?
Windows uses “tracert,” while MacOS and Linux use “traceroute.” The function and output are essentially the same.
Why do I see asterisks (*) in my traceroute results?
These mean the router didn’t reply in time. It could be down, busy, or set up to ignore traceroute requests.
Can server location really make my website faster?
Absolutely! Hosting closer to your visitors can cut latency dramatically. For global reach, use a CDN.
What should I do when traceroute shows high latency at one hop?
That’s usually where the problem is. Share this info with your hosting provider or ISP so they can fix it.
Is it safe to use traceroute at work?
Yes, if your company allows it for troubleshooting. Never use it on networks you don’t own or have approval to test.
By learning the traceroute command, you’ve got a powerful tool for making your online world smoother, faster, and more reliable.
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
