
Modern software is updated frequently. Applications receive new features, bug fixes, and security improvements without long delays or major disruptions. This smooth process is made possible by CI/CD, a core practice in modern software development.
CI/CD focuses on automating how code is built, tested, and delivered. Instead of waiting weeks or months to release updates, teams can ship changes quickly and safely. This approach improves quality, reduces errors, and allows software to evolve continuously.
This guide explains what CI/CD is, how it works, and why it matters, using clear and simple language for a general audience.
What Does CI/CD Mean?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery. Sometimes, the second “CD” also refers to Continuous Deployment.
- Continuous Integration (CI) means regularly adding small pieces of code into a shared project. It is the practice of frequently adding code changes to a shared codebase.
- Continuous Delivery (CD) means automatically preparing that code so it’s always ready to be released. It ensures that code changes are automatically prepared and ready for release.
- Continuous Deployment takes it one step further by releasing updates automatically and releasing every approved change to users.
In short, CI/CD helps teams deliver better software faster and with fewer problems. Together, CI/CD creates a fast and reliable way to deliver software updates.

Why CI/CD Is Important
Modern software systems evolve continuously, with frequent updates, fixes, and improvements being released over time. Without a clear and automated process, these changes can lead to errors, service interruptions, or unstable applications, making it difficult to maintain reliability and user trust.
CI/CD introduces a structured workflow that automates how changes are tested and delivered, ensuring updates are applied smoothly and consistently.
CI/CD is important because it:
- Reduces manual work by automating repetitive tasks like testing, building, and deployment, minimizing human effort and mistakes.
- Detects problems early through automated checks that identify bugs and issues as soon as changes are introduced.
- Improves software stability by ensuring every update passes predefined quality checks before moving forward.
- Speeds up delivery by allowing teams to release updates more frequently without long development or release cycles.
- Encourages consistent development practices by following standardized processes that keep workflows predictable and organized.
By automating key steps, teams can focus on improving features instead of fixing preventable issues.
What Is Continuous Integration?
Continuous Integration is a development practice that emphasizes merging code changes into a shared codebase on a regular basis. Instead of working in isolation for long periods, teams integrate updates frequently, which helps maintain code quality and reduces the risk of unexpected issues.
By continuously validating changes through automation, Continuous Integration ensures that the codebase remains stable and easy to maintain.
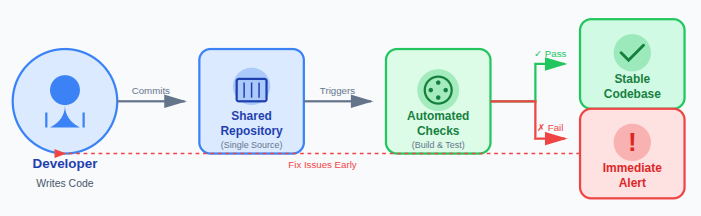
Each time a change is made:
- The code is added to a shared repository so all team members work from a single, updated source of truth.
- Automated checks are triggered to verify that the new changes meet predefined quality and build requirements.
- Errors are detected immediately, allowing teams to fix issues early before they grow into larger problems.
This approach prevents large integration problems and keeps the codebase stable.
Key point: Continuous Integration encourages small, frequent updates, making changes easier to manage and reducing the risk associated with large code merges.
What Is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Delivery is a development practice that ensures software is always ready to be released at any time. It focuses on automating the steps that prepare code for deployment, making the release process predictable, safe, and low risk.
By keeping applications in a deployable state, Continuous Delivery helps teams avoid last-minute issues and maintain consistent release quality.
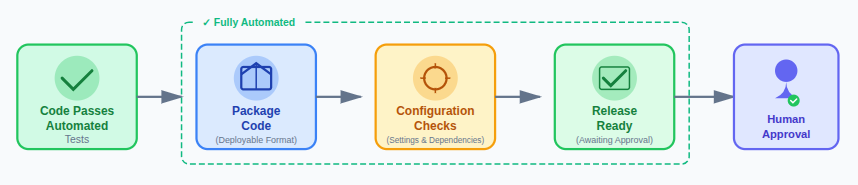
After passing automated tests:
- The code is packaged into a deployable format that can be consistently used across environments.
- Configuration checks are applied to confirm that settings, dependencies, and environment variables are correctly defined.
- The software is prepared for release so it can be deployed quickly whenever approval is given.
Human approval may still be required before deployment, but all technical steps are handled automatically to ensure reliability and consistency.
Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment
Although they are closely related, these terms are not the same.
- Continuous Delivery: Code is ready to be released at any time, but deployment is a manual decision.
- Continuous Deployment: Code is automatically released once all checks pass.
| Aspect | Continuous Delivery | Continuous Deployment |
| Definition | Ensures software is always ready for release but requires manual approval to deploy | Automatically deploys every approved change without human intervention |
| Deployment Trigger | Deployment starts after a human decision or business approval | Deployment happens automatically once all checks pass |
| Level of Automation | Build, test, and release preparation are automated | Build, test, and deployment are fully automated |
| Human Involvement | Required at the final deployment stage | Not required once the pipeline is configured |
| Risk Control | Allows teams to review changes before releasing | Relies entirely on automated tests to manage risk |
| Release Frequency | Frequent but controlled releases | Very frequent or continuous releases |
| Best Suited For | Teams needing compliance, approvals, or controlled rollouts | Teams confident in automation and rapid iteration |
| Rollback Handling | Rollbacks are typically triggered manually if needed | Rollbacks are often automated as part of the pipeline |
| Complexity | Easier to implement and manage | More complex due to full automation |
| Goal | Keep software deployable at all times | Release changes to users as quickly as possible |
The choice depends on business needs, risk tolerance, and compliance requirements.
How CI/CD Works
CI/CD follows a structured and automated workflow that moves code changes smoothly from development to release. Each step in the process is designed to verify quality, reduce risk, and ensure that updates are delivered in a reliable and repeatable way.
By validating changes continuously, CI/CD helps teams maintain consistency while releasing improvements with confidence.
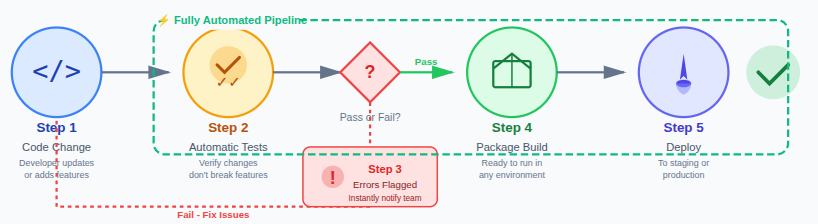
Here’s a simple flow of how CI/CD works:
- A change is made to the code when a developer updates or adds new functionality to the application.
- The system runs automatic tests to verify that the new changes do not break existing features.
- Errors are flagged instantly so issues can be fixed before the code moves forward in the pipeline.
- Approved code is packaged into a build that is ready to run in different environments.
- The update is delivered or deployed to a staging or production environment based on the release process.
It’s like an automatic quality checker that never gets tired. Each step is designed to catch errors early and maintain consistency.
CI/CD Pipeline Explained
A CI/CD pipeline is an automated workflow that guides code through a series of defined stages before it is released. Each stage validates the code in a controlled manner, ensuring quality, consistency, and reliability throughout the delivery process.
By standardizing these steps, CI/CD pipelines reduce manual intervention and make software releases predictable and repeatable.
Common pipeline stages include:
- Code validation to check that the submitted changes meet coding standards and basic quality rules.
- Automated testing to verify functionality and prevent existing features from breaking.
- Build creation to compile and package the code into a deployable format.
- Deployment preparation to configure environments and confirm readiness for release.
- Release execution to deliver the approved build to the target environment.
Pipelines ensure repeatable and reliable delivery processes.
Key Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
A CI/CD pipeline represents the complete path that code follows from initial development to final release. Each component plays a specific role in maintaining software quality while ensuring updates move quickly and smoothly through the delivery process.
Together, these components create a structured system that balances speed, reliability, and consistency.
Main components include:
- Source control: Stores and manages code changes in a shared repository, allowing teams to collaborate and track updates effectively.
- Build process: Transforms the source code into a runnable or deployable format by compiling and packaging required resources.
- Automated testing: Runs predefined tests to identify bugs, performance issues, or compatibility problems early.
- Deployment stage: Delivers the approved build to the target environment so users can access the latest updates.
Each component works together to protect both software quality and delivery speed.
Benefits of CI/CD
CI/CD offers a structured and automated approach to software delivery that benefits everyone involved in the development process. By reducing manual effort and standardizing workflows, it helps teams release updates more efficiently while maintaining reliability.
Over time, CI/CD builds trust in the release process and improves overall delivery confidence.
Major benefits include:
- Faster software releases by automating build, test, and deployment steps, reducing delays between updates.
- Reduced risk of failures through early detection of issues before they reach production.
- Higher code quality by enforcing consistent testing and validation for every change.
- Better collaboration as teams work with a shared process and clear visibility into changes.
- Predictable delivery schedules that make planning and releases more reliable and less stressful.
Consistent use of CI/CD strengthens stability and confidence in every software release.

Popular CI/CD Tools
CI/CD tools are designed to automate the processes involved in building, testing, and delivering software. They help teams reduce manual effort, maintain consistent workflows, and ensure that every code change follows the same quality standards.
By using the right CI/CD tool, teams can streamline development processes and improve the reliability of software releases.
Some widely used options include:
- Jenkins: A flexible automation server that supports custom pipelines through a large ecosystem of plugins.
- GitHub Actions: A native GitHub feature that enables automated workflows directly within repositories.
- GitLab CI: An integrated CI/CD solution that manages code, pipelines, and deployments in a single platform.
- CircleCI: A cloud-based service focused on fast execution and easy pipeline configuration.
- Bitbucket Pipelines: A built-in CI/CD tool for Bitbucket that simplifies automation using repository-based pipelines.
These tools automate repetitive tasks and help enforce consistent, reliable development workflows.
Automation in CI/CD
Automation is the core element that makes CI/CD effective and reliable. By replacing manual processes with automated workflows, teams can deliver updates faster while maintaining consistent quality across all stages of development and deployment.
Automated processes ensure that every change is handled the same way, reducing risk and improving overall system stability.
Automated systems handle:
- Code testing to verify functionality and detect issues without manual intervention.
- Build creation to consistently compile and package code into deployable formats.
- Deployment steps to move approved changes through environments in a controlled manner.
- Monitoring and reporting to track performance, failures, and pipeline results in real time.
Automation minimizes human error and ensures dependable outcomes across different environments.
Server Management in CI/CD Automation
CI/CD automation relies heavily on stable and consistently configured servers to run builds, tests, and deployments smoothly. If server environments are misconfigured or unmanaged, even well-designed pipelines can fail.
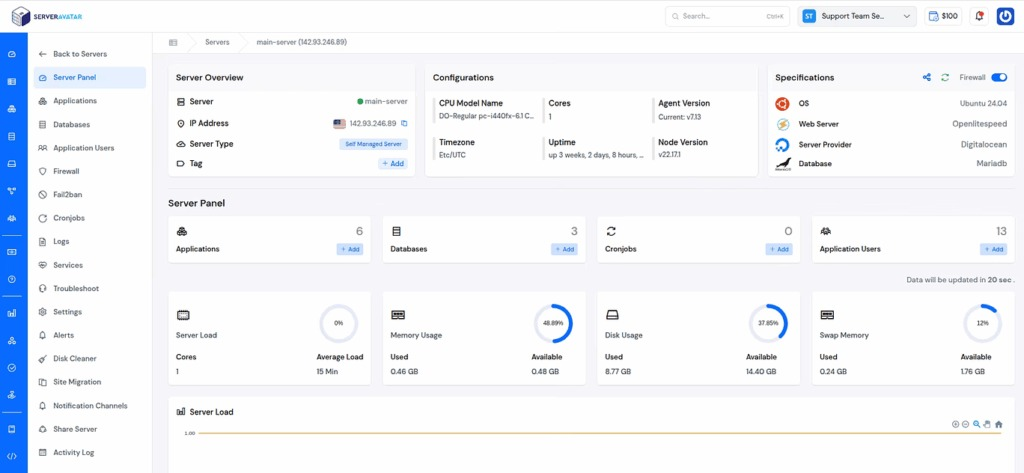
ServerAvatar supports CI/CD workflows by simplifying server and application management through a centralized dashboard. It helps teams maintain consistent environments, manage services, and monitor applications, allowing CI/CD pipelines to operate reliably without manual server intervention.
What is ServerAvatar?
ServerAvatar is a platform to simplify the hosting and management of servers and applications. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing PHP and Node.js based web applications on servers.
Security in CI/CD
Security plays a critical role in CI/CD by ensuring that software is not only functional but also safe to deploy. Integrating security checks directly into the pipeline helps identify vulnerabilities early and prevents risky code from moving forward.
By addressing security throughout the development process, teams can reduce exposure to threats and maintain trust in their releases.
Modern pipelines include:
- Automated security scans to identify vulnerabilities and unsafe patterns within the codebase.
- Dependency checks to detect outdated or insecure third-party libraries used in the application.
- Access control rules to restrict who can modify code, pipelines, or deployment settings.
- Audit logs to maintain a clear record of changes, approvals, and deployment activity.
By integrating security early in the CI/CD process, teams reduce risks before software reaches users.
CI/CD in Practice
CI/CD can be understood as a structured workflow where changes move through automated checks before being released. Instead of relying on manual reviews and delayed testing, every update follows the same controlled process to ensure quality and readiness.
This approach keeps software continuously validated and prepared for release.
In a CI/CD workflow:
- Changes are made in small increments, so updates are easier to test and manage.
- Automated checks run immediately to verify that each change meets quality and functionality standards.
- The application remains release-ready because approved changes are consistently validated and prepared for deployment.
This structured process ensures reliability and consistency throughout the software delivery lifecycle.
Common CI/CD Challenges
Although CI/CD significantly improves software delivery, implementing it effectively can present certain challenges. These issues often arise during adoption and can impact the stability or efficiency of the pipeline if not addressed early.
With careful planning and a phased approach, most CI/CD challenges can be managed successfully.
Common issues include:
- Poor test coverage which reduces the effectiveness of automated checks and allows bugs to pass through the pipeline.
- Complex setup caused by integrating multiple tools, environments, and workflows.
- Resistance to change when teams are hesitant to move away from familiar manual processes.
- Inconsistent processes that lead to unpredictable results and deployment issues.
Addressing these challenges gradually helps teams build a reliable and sustainable CI/CD workflow.
CI/CD Best Practices
Following best practices helps teams get the most value from CI/CD while maintaining stability and reliability. A well-defined approach ensures that automation works as intended and that issues are identified and resolved quickly.
Consistent execution of these practices leads to smoother workflows and more dependable software releases.
To use CI/CD effectively:
- Keep changes small and frequent to reduce risk and make issues easier to identify and fix.
- Automate testing thoroughly to ensure every update meets quality standards before moving forward.
- Monitor deployments closely to quickly detect performance issues or unexpected behavior.
- Fix failures immediately to prevent problems from spreading through the pipeline.
- Maintain clear documentation so teams understand workflows, responsibilities, and recovery steps.
Consistency and discipline are essential for achieving long-term success with CI/CD.
The Future of CI/CD
CI/CD is continuously evolving to meet the growing demands of modern software development. As applications become more complex and release cycles shorten, CI/CD practices are adapting to deliver faster, safer, and more reliable updates.
These advancements ensure that CI/CD remains essential as software continues to play a critical role across industries.
CI/CD continues to evolve with:
- Advanced automation that reduces manual intervention and increases pipeline efficiency.
- Improved monitoring to provide better visibility into performance, failures, and deployment outcomes.
- Stronger security integration that embeds security checks directly into every stage of the pipeline.
- Smarter pipelines that adapt dynamically based on project needs and system behavior.
As software becomes more central to daily life, CI/CD will remain a core and evolving development practice.
FAQs
1. What does CI/CD stand for?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery. In some cases, CD also refers to Continuous Deployment, where changes are released automatically.
2. Is CI/CD only useful for large development teams?
No. CI/CD is beneficial for teams of all sizes. Even small teams benefit from automation, early error detection, and consistent delivery processes.
3. Is CI/CD secure?
CI/CD can be very secure when security checks are integrated into the pipeline, including vulnerability scans, dependency checks, access controls, and audit logs.
4. What are common mistakes when adopting CI/CD?
Common mistakes include poor test coverage, overly complex pipelines, ignoring failures, and trying to automate everything at once instead of gradually.
5. Is CI/CD difficult to maintain long term?
Not if best practices are followed. Keeping pipelines simple, monitoring regularly, fixing issues quickly, and maintaining clear documentation helps ensure long-term success.
Conclusion
CI/CD has become a foundational practice in modern software development because it enables teams to deliver updates faster, safer, and more consistently. By automating the processes of building, testing, and releasing code, CI/CD reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and ensures that software is always in a ready-to-deploy state.
Whether you are working on a small application or managing complex systems, CI/CD helps maintain stability while allowing continuous improvement. When supported by reliable automation, strong security practices, and effective server management tools like ServerAvatar, CI/CD workflows become easier to manage and scale over time.
As software continues to evolve rapidly, adopting CI/CD is no longer optional, it is an essential approach for delivering high-quality software with confidence.
Stop Wasting Time on Servers. Start Building Instead.
You didn’t start your project to babysit servers. Let ServerAvatar handle deployment, monitoring, and backups — so you can focus on growth.
Deploy WordPress, Laravel, N8N, and more in minutes. No DevOps required. No command line. No stress.
Trusted by 10,000+ developers and growing.
