
Have you ever wondered how popular websites handle thousands of tasks simultaneously without slowing down? The secret lies in laravel automation using background job processing – and today, we’re diving deep into how Laravel’s queue system paired with Supervisor can transform your web application from sluggish to lightning-fast.
Think of your web application like a busy restaurant. Without proper queue management, it’s like having one chef trying to prepare every order while customers wait. But with Laravel queues and Supervisor working together, it’s like having a well-organized kitchen with multiple chefs working efficiently behind the scenes while customers enjoy quick service.
What Are Laravel Queues and Why Do You Need Them?
Laravel queues are your application’s way of saying “I’ll handle this later” to time-consuming tasks. Instead of making users wait while your app sends emails, processes images, or generates reports, queues push these tasks to the background.
Real-World Benefits of Queue Systems
When you implement queues properly, you’ll notice immediate improvements:
- Faster page loads – Users don’t wait for heavy operations
- Better user experience – No more spinning wheels of death
- Improved scalability – Handle more concurrent users
- System reliability – Failed tasks can be retried automatically
Common Use Cases for Laravel Queues
Your application can benefit from queues in numerous scenarios:
- Email notifications and marketing campaigns
- Image and video processing operations
- Data import/export functionality
- Third-party API calls that might be slow
- Database cleanup and maintenance tasks
Understanding Supervisor: Your Queue Management Hero
Supervisor is like having a dedicated manager for your background workers. While Laravel creates the jobs, Supervisor ensures those jobs keep running, restart if they fail, and scale when needed.
Why Supervisor Matters for Your Laravel Application
Without Supervisor, your queue workers are vulnerable. If a worker crashes, stops, or encounters an error, your background jobs pile up like dishes in a sink. Supervisor acts as your reliable assistant, always watching and maintaining your workers.
Key Features That Make Supervisor Essential
Supervisor brings several powerful capabilities to your Laravel setup:
- Automatic restart of crashed workers
- Process monitoring and health checks
- Easy scaling by running multiple workers
- Centralized configuration management
- Detailed logging and error tracking
The Perfect Marriage: Laravel Queues + Supervisor
Combining Laravel queues with Supervisor creates a robust, production-ready system. Laravel handles the job creation and processing logic, while Supervisor manages the worker processes that execute these jobs.
This partnership ensures your background tasks run reliably, scale efficiently, and recover gracefully from failures. It’s the difference between hoping your jobs complete and knowing they will.
Setting Up Your Laravel Queue System
Configuring Your Queue Driver
First, you need to choose and configure your queue driver in Laravel. Open your .env file and set up your preferred driver:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis
REDIS_HOST=127.0.0.1
REDIS_PASSWORD=null
REDIS_PORT=6379If you are using ServervAvatar, you will get Redis Password Here.
Creating Your First Job
Generate a new job class using Laravel’s artisan command:
php artisan make:job ProcessUserRegistrationDispatching Jobs to Your Queue
Once your job is created, you can dispatch it from anywhere in your application:
ProcessUserRegistration::dispatch($user);Installing and Configuring Supervisor
System Installation
Installing Supervisor varies by operating system. For Ubuntu/Debian systems:
sudo apt-get install supervisorFor CentOS/RHEL:
sudo yum install supervisorStarting Supervisor Service
After installation, start and enable the Supervisor service:
sudo systemctl start supervisord
sudo systemctl enable supervisordCreating Your First Supervisor Configuration
Understanding Configuration Structure
Create a new configuration file for your Laravel queues:
[program:laravel-queue-worker]
process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02d
command=php /path/to/your/laravel/artisan queue:work redis --sleep=3 --tries=3 --max-time=3600
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stopasgroup=true
killasgroup=true
user=www-data
numprocs=4
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/path/to/your/laravel/storage/logs/worker.log
stopwaitsecs=3600Key Configuration Parameters Explained
Understanding each parameter helps you optimize your setup:
- process_name: Unique identifier for each worker process
- command: The actual Laravel queue command to execute
- numprocs: Number of worker processes to run
- autostart: Automatically start workers when Supervisor starts
- autorestart: Restart workers if they crash or stop

Advanced Supervisor Configuration Options
Environment-Specific Settings
Different environments require different configurations. For production environments, consider these settings:
[program:laravel-queue-production]
environment=LARAVEL_ENV=production
priority=999
startsecs=10
startretries=3Memory and Resource Management
Prevent memory leaks by configuring process limits:
[program:laravel-queue-worker]
; Restart after processing 1000 jobs
command=php /path/to/artisan queue:work --max-jobs=1000
; Restart after 1 hour
command=php /path/to/artisan queue:work --max-time=3600Monitoring and Managing Your Queue Workers
Using Supervisor Control Commands
Supervisor provides several commands for managing your workers:
# Check status of all programs
sudo supervisorctl status
# Restart specific program
sudo supervisorctl restart laravel-queue-worker:*
# Start/stop programs
sudo supervisorctl start laravel-queue-worker:*
sudo supervisorctl stop laravel-queue-worker:*If you are using ServerAvatar, you can directly restart any specific program from the Dashboard, as shown in the image below.
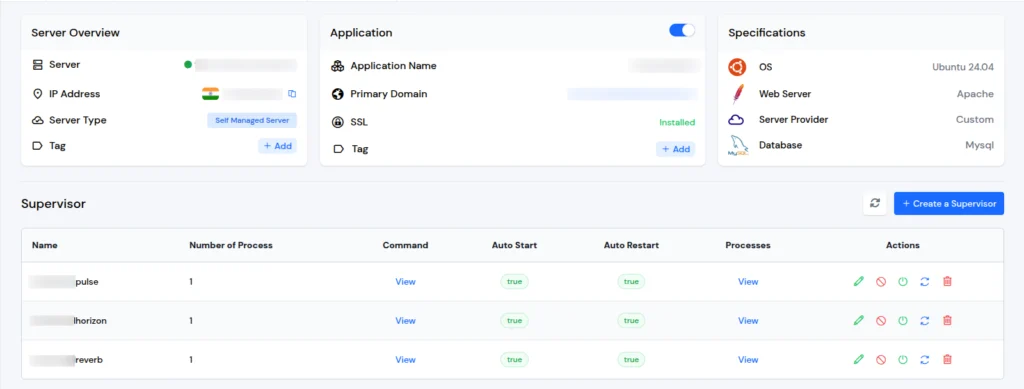
Real-Time Monitoring
Monitor your queue workers in real-time using Laravel’s built-in commands:
# Monitor queue status
php artisan queue:monitor redis:default --max=100
# View failed jobs
php artisan queue:failedHandling Failed Jobs and Error Recovery
Configuring Retry Logic
Set up intelligent retry mechanisms in your Supervisor configuration:
[program:laravel-queue-worker]
command=php /path/to/artisan queue:work --tries=3 --backoff=10,30,60Failed Job Management
Laravel provides excellent tools for managing failed jobs:
# Retry all failed jobs
php artisan queue:retry all
# Retry specific failed job
php artisan queue:retry 5
# Clear failed jobs
php artisan queue:flushScaling Your Queue System for High Traffic
Horizontal Scaling with Multiple Workers
Increase the numprocs value in your Supervisor configuration to handle higher loads:
[program:laravel-high-traffic]
numprocs=8
process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02dQueue Prioritization
Set up different workers for different queue priorities:
[program:laravel-high-priority]
command=php /path/to/artisan queue:work --queue=high,default
priority=1000
[program:laravel-low-priority]
command=php /path/to/artisan queue:work --queue=low
priority=500Security Best Practices for Queue Management
User Permissions and Access Control
Always run queue workers with appropriate user permissions:
[program:laravel-queue-secure]
user=laravel-user
directory=/var/www/laravel
umask=022Secure Configuration Management
Protect your configuration files and ensure proper file permissions:
sudo chown root:root /etc/supervisor/conf.d/laravel-queue.conf
sudo chmod 644 /etc/supervisor/conf.d/laravel-queue.confTroubleshooting Common Issues
Worker Process Not Starting
If your workers aren’t starting, check these common issues:
- File permissions on your Laravel application
- PHP path in the command configuration
- Environment variables and database connections
- Log files for specific error messages
Memory and Performance Issues
Monitor and resolve memory-related problems:
# Check memory usage
ps aux | grep "queue:work"
# Monitor system resources
top -p $(pgrep -d',' -f "queue:work")Performance Optimization Tips
Database Connection Optimization
Optimize database connections for queue workers:
// In your job class
public function handle()
{
DB::connection()->getPdo()->setAttribute(
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_USE_BUFFERED_QUERY,
false
);
// Your job logic here
}Memory Management Best Practices
Implement memory-conscious coding in your jobs:
- Unset large variables after use
- Use database chunking for large datasets
- Implement garbage collection calls when needed
- Monitor memory usage during development
Using ServerAvatar for Simplified Management
If you’re using ServerAvatar for server management, you can streamline your Supervisor setup significantly. ServerAvatar provides a user-friendly interface for managing Supervisor processes without diving into configuration files.
Benefits of ServerAvatar Integration
ServerAvatar simplifies queue management by offering:
- Visual process management through a web interface
- Easy configuration without manual file editing
- Real-time monitoring and alerting
- Automated deployment integration
You can directly create a supervisor process from ServerAvatar’s dashboard. For detailed instructions on setting up Supervisor processes through ServerAvatar, check out their comprehensive documentation at: https://serveravatar.com/docs/application/supervisor
This approach is particularly valuable for teams who prefer graphical interfaces over command-line management, making queue supervision accessible to developers of all skill levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many queue workers should I run for my Laravel application?
The optimal number of workers depends on your server resources and job complexity. Start with 2-4 workers and monitor CPU and memory usage. Increase workers if jobs are piling up, but ensure you don’t overwhelm your database or external services with too many concurrent connections.
What happens if my Supervisor process crashes?
Supervisor is designed to be highly reliable, but if it crashes, your queue workers will stop processing jobs. Set up system-level monitoring to restart Supervisor automatically, and consider using process monitoring tools like Monit or systemd to ensure Supervisor itself stays running.
Can I use different queue drivers with the same Supervisor configuration?
Yes, you can run multiple Supervisor programs with different queue drivers. Create separate configuration files for each driver (Redis, database, SQS, etc.) and adjust the Laravel artisan commands accordingly. This approach allows you to distribute different types of jobs across various queue systems.
How do I handle jobs that take longer than expected to complete?
Configure appropriate timeout values in both Laravel and Supervisor. Use the --timeout parameter in your Laravel queue command and set stopwaitsecs in Supervisor configuration. For genuinely long-running jobs, consider breaking them into smaller chunks or using dedicated long-running worker processes.
Is it safe to restart queue workers while jobs are running?
Supervisor handles graceful shutdowns by sending SIGTERM signals to worker processes, allowing them to finish current jobs before stopping. However, set appropriate stopwaitsecs values to prevent indefinite waiting. For critical jobs, implement proper cleanup and resumption logic to handle unexpected interruptions.
Conclusion
Implementing Laravel queues with Supervisor transforms your application from a single-threaded bottleneck into a multi-processing powerhouse. This combination provides reliability, scalability, and performance that modern web applications demand.
The journey from basic queue setup to advanced Supervisor configuration might seem complex initially, but the benefits are immediate and substantial. Your users will notice faster response times, your servers will handle more concurrent requests, and your application will become more resilient to failures.
Remember that queue management is not a “set it and forget it” solution. Regular monitoring, optimization, and maintenance ensure your background job processing remains efficient and reliable as your application grows.
Whether you choose manual configuration or tools like ServerAvatar for simplified management, the key is starting with a solid foundation and iterating based on your application’s specific needs.
