Deploy from GitLab
Creating an application in ServerAvatar for hosting PHP scripts and projects with Git is simple. You can specify the application name, domain, system user, and other options such as PHP version and custom web root. When choosing the deployment method, you can select "Git" to easily deploy your PHP code from a Git repository. Once the application is created, ServerAvatar will automatically clone the repository and deploy the code. You can manage the Git deployment process from the ServerAvatar dashboard. ServerAvatar makes it easy to create and manage PHP applications with Git.
Once you have connected your server with ServerAvatar, you can follow the steps below to automatically install the GitLab repository on your server.
GitLab Integration
Step 1: First, you need to Integrate Git with your ServerAvatar account, log in to your ServerAvatar account and click on the Integration option in the left-hand side menu of the ServerAvatar panel.

Step 2: Click on the Gitlab Link Gitlab button under the Git section as shown in the image below. After that, authorize ServerAvatar to deploy your project and connect your GitLab account with the ServerAvatar account.
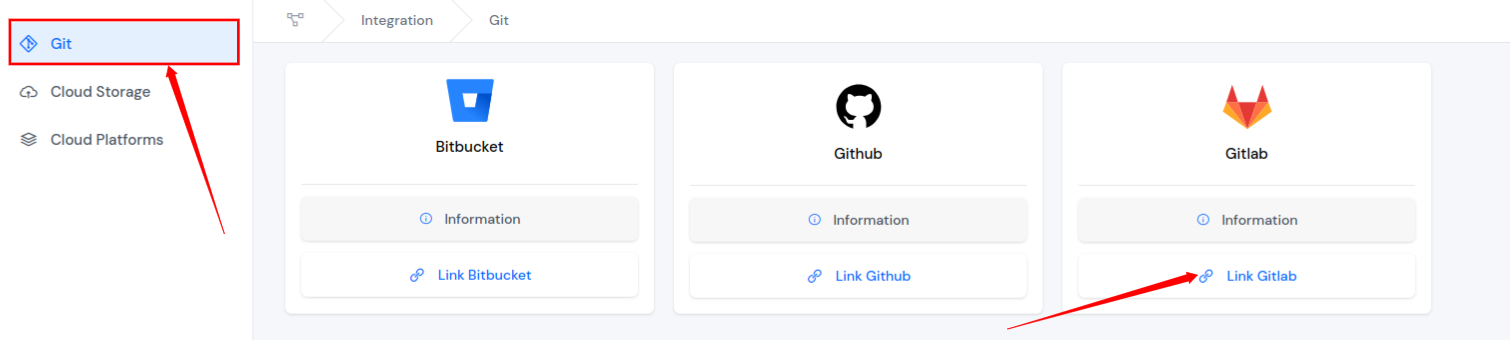
Step 3: Now, you can deploy a site from Gitlab.
Create Application
Step 1: Click on the server on which you want to create the new application.
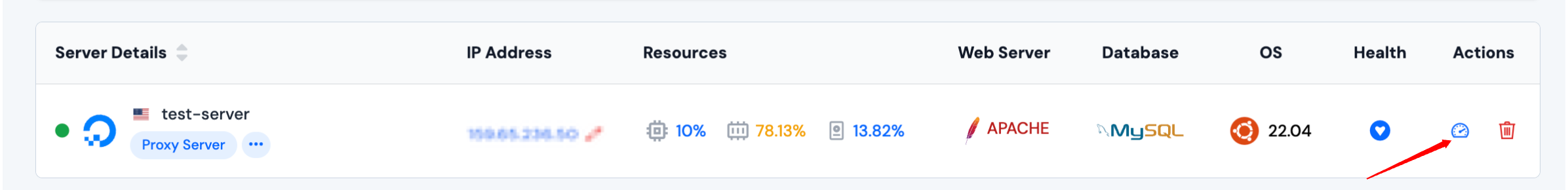
Step 2: You will now see the Applications option on the left-hand sidebar of the Server Panel. Click on Applications.
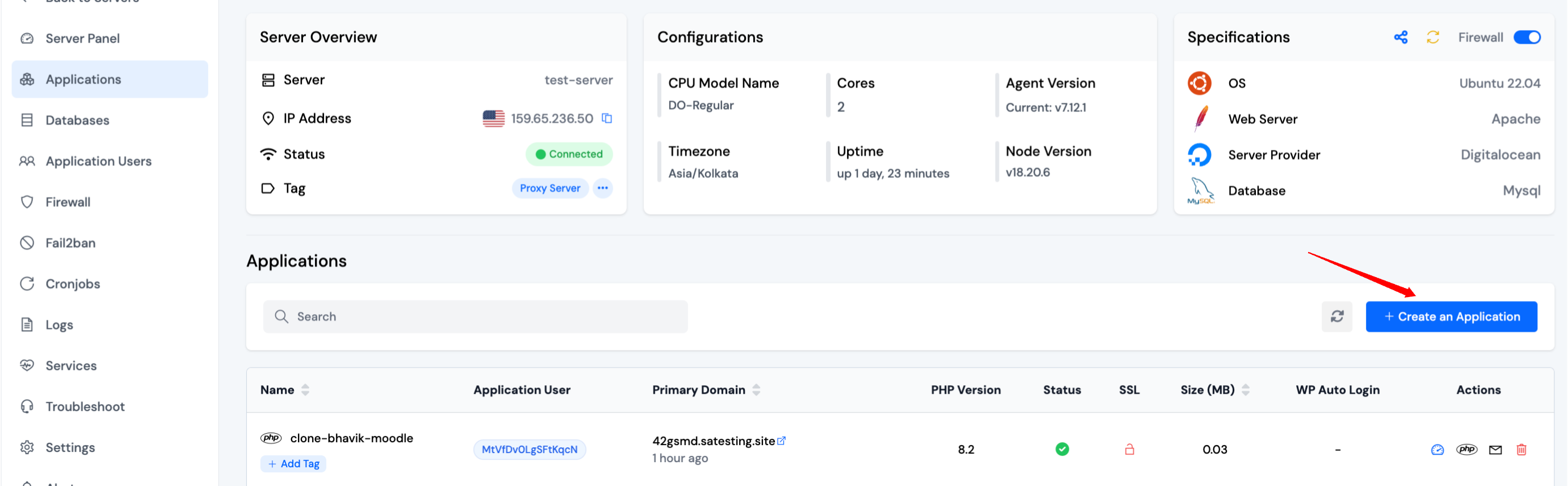
Step 3: You will now see the Applications table like the image below. Click on the Create an Application button on the top right of the Applications table, as mentioned in the below image.
Step 4: Basic Details
- Enter the name of your application in the Application Name field.
- Choose whether you want to use a primary domain or a test domain in the Domain field. If you select a test domain, you can change it later to a primary domain.
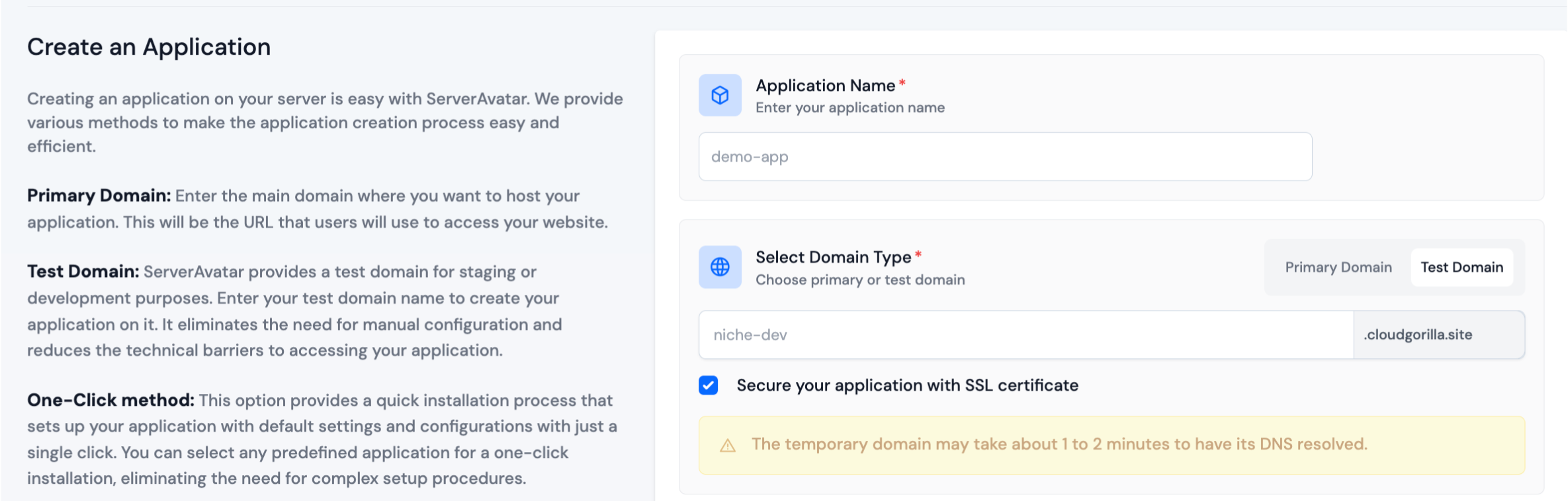
Step 5: Application
-
Choose the method Git to deploy using git.
-
In the Git method, you have to select the Git provider as GitLab.
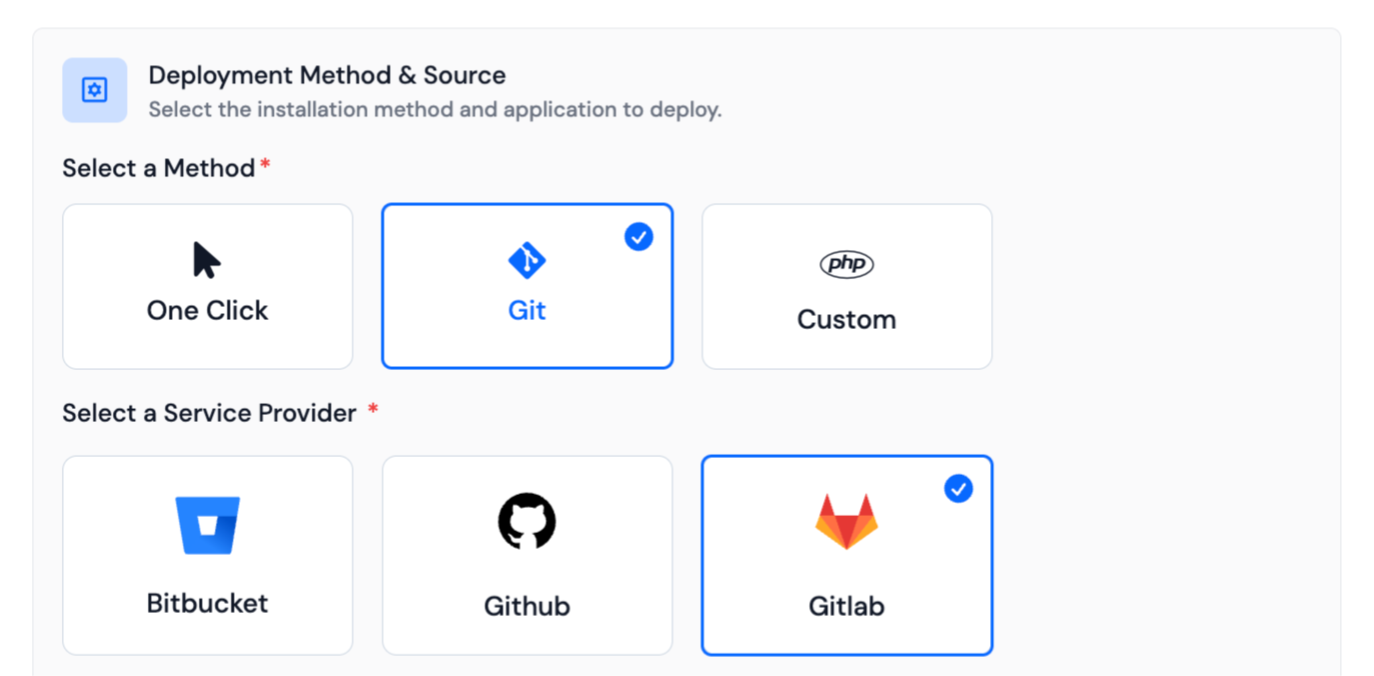
-
If your repository Type is Public, then enter the Clone HTTP URL, Branch, and if you want to run a script after cloning your repository, then write a deployment script. Then click on the Next Step button.
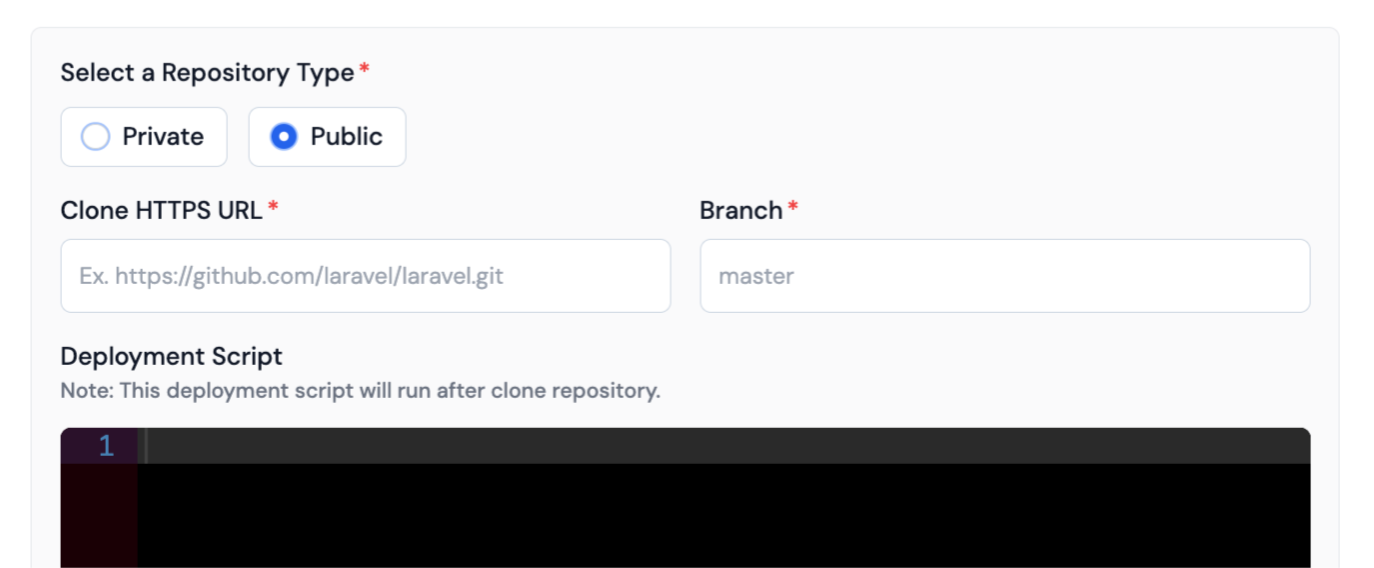
-
If your repository Type is Private, then first, you need to Generate SSH-Key for deployment and Copy that ssh-key to put into the Gitlab account,
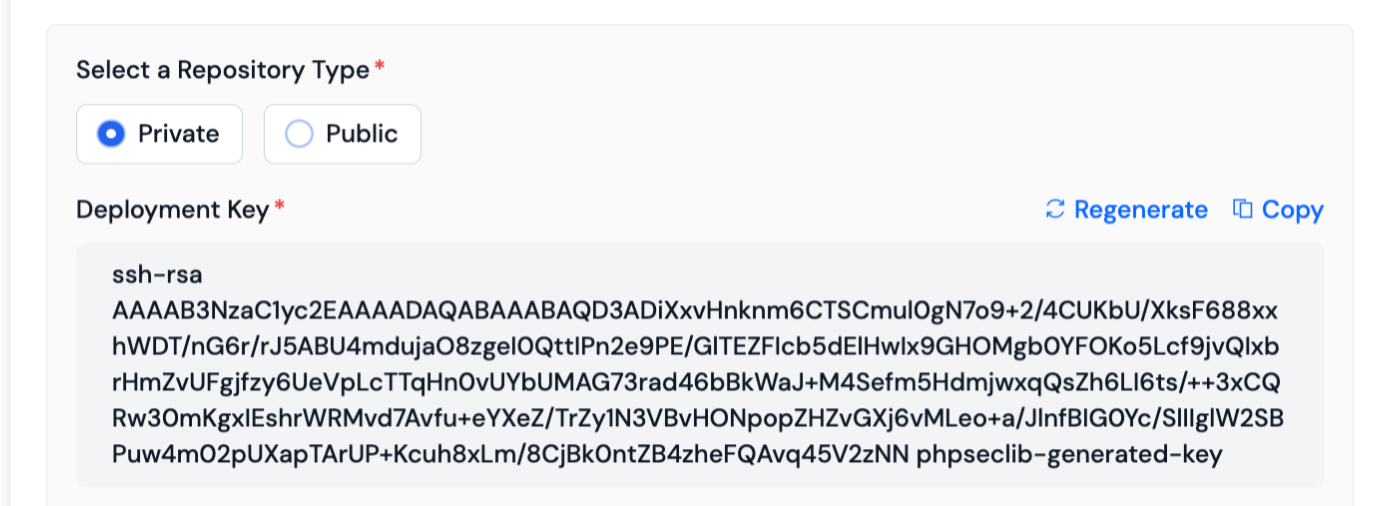
-
Login into your Integrated Gitlab Account, and Navigate to Edit Profile → SSH Keys.
-
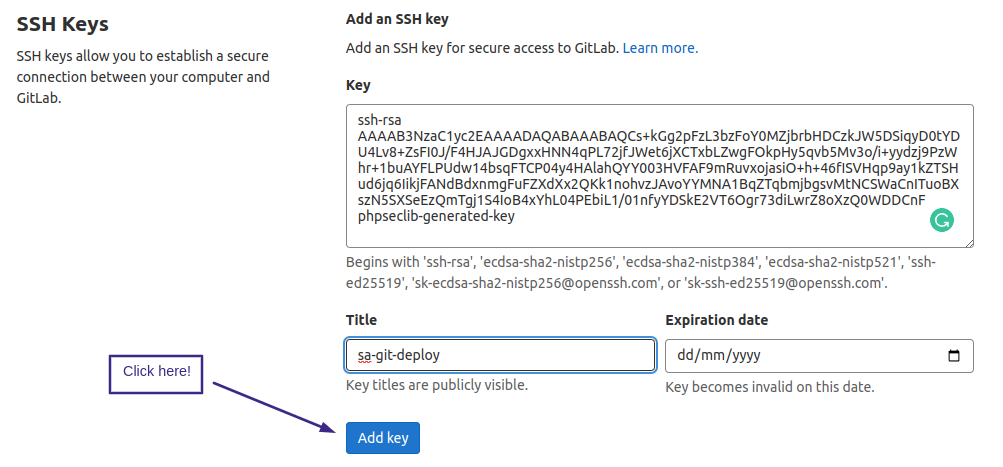
Enter Title and Paste your Generated SSH-Key as shown in the image below.
-
Then click on the Add Key button.
-
After that, select Integrated Account, then select your repository Repository and select its Branch. If you want to run script after clone your repository then write a deployment script.
Step 6: Log Monitoring Suite
-
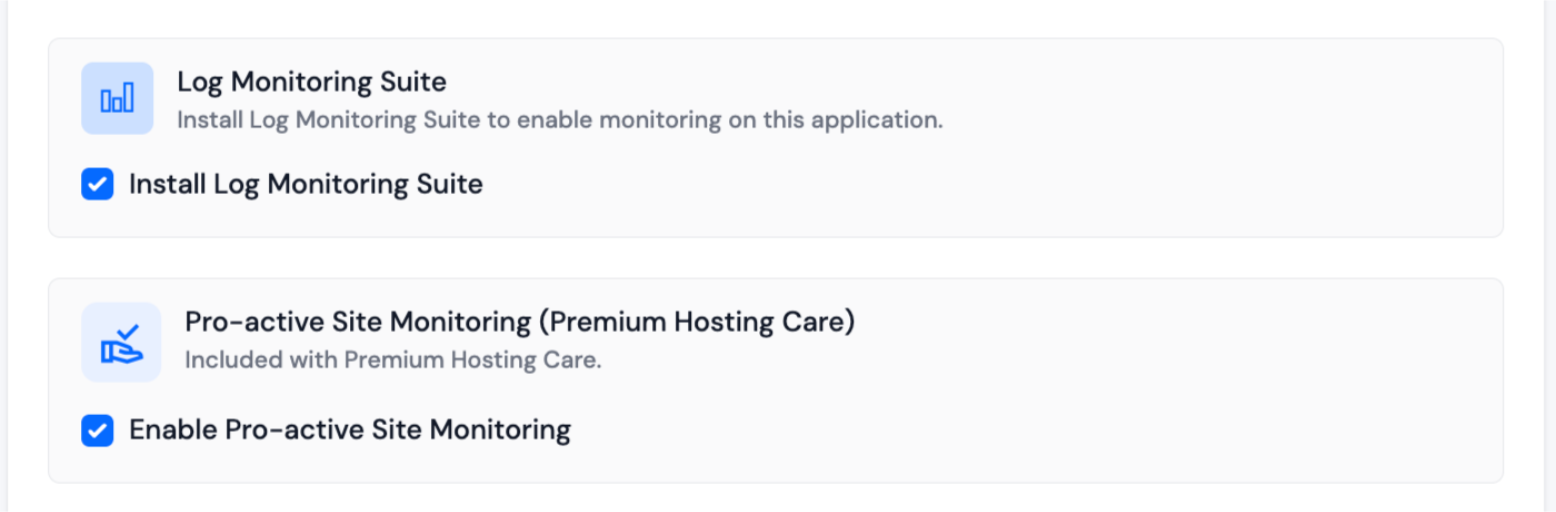
If you have purchased the Log Monitoring Suite, you will see a checkbox option to Install Log Monitoring Suite on this application.
-
Check this option if you want to enable log monitoring for your application. This will allow you to monitor and analyze application logs directly from the ServerAvatar dashboard.
Step 7: Pro-active Site Monitoring (Premium Hosting Care)
-
If you have purchased Premium Hosting Care, you will see a checkbox option to Enable Pro-active Site Monitoring on this application.
-
Check this option if you want to enable pro-active site monitoring for your application. Premium Hosting Care provides top-tier server management. Enjoy high-priority support, optimization, app-level troubleshooting, proactive monitoring, and a dedicated Slack channel for real-time assistance.
-
If you haven't purchased Premium Hosting Care yet, you can learn how to purchase Premium Hosting Care from the Add-ons section.
Step 8: Advance Options
-
Click on Show Advanced Options to access additional configuration settings for your application.
-
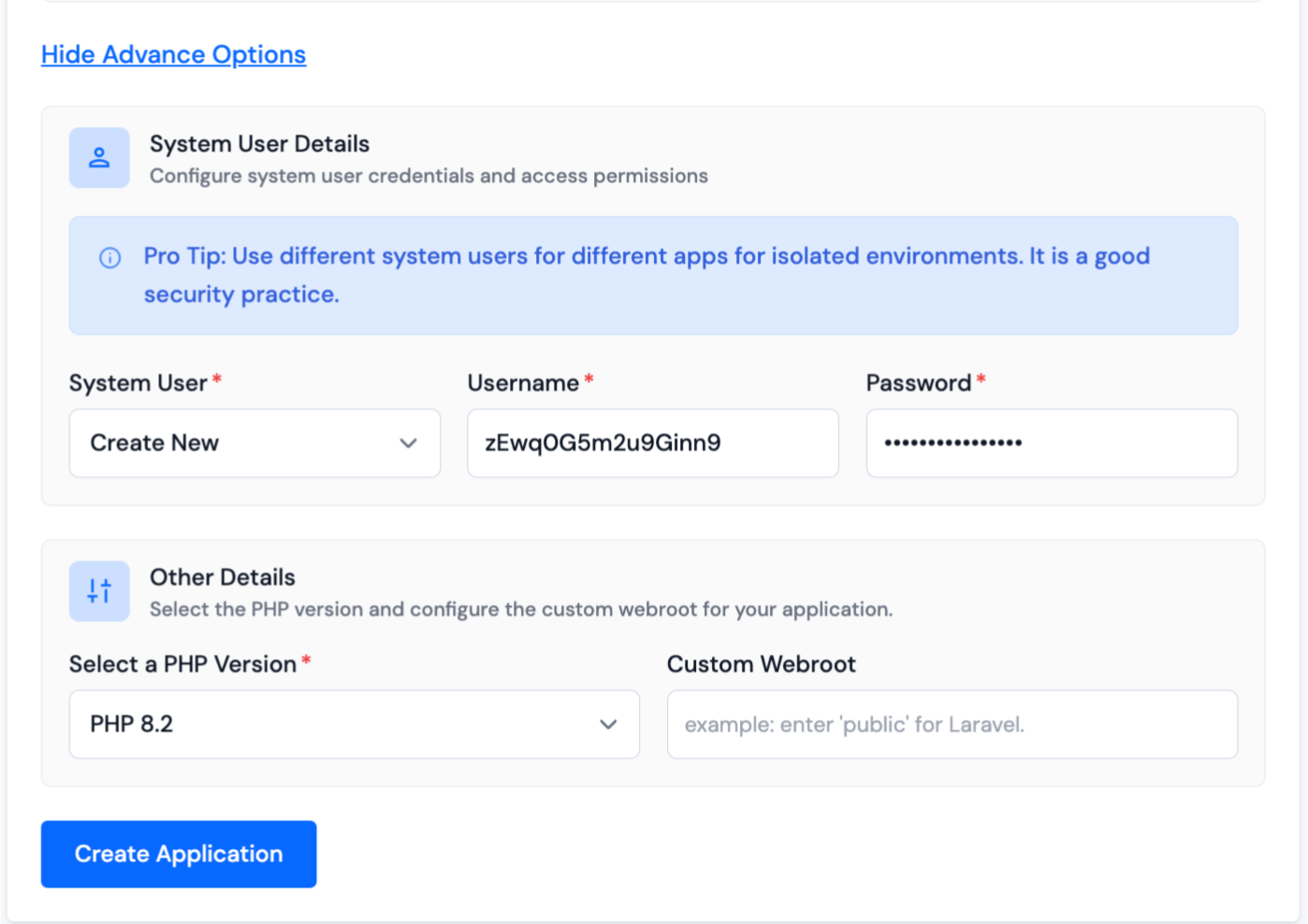
When creating a new application in ServerAvatar, you have the option to either create a new system user for the application or use an existing one. A system user is a user account created on your server, which is used to manage files and permissions for your application.
-
In the Basic Settings section of creating an application in ServerAvatar, you have the option to select the PHP version for your application. ServerAvatar supports multiple PHP versions ranging from 7.2 to 8.4. You can choose the desired PHP version for your application.
-
You also have the option to specify a custom webroot path for your application. By default, ServerAvatar sets the webroot path to /public_html for your application. However, if you want to set a custom webroot path, you can do so by entering the desired path in the "Webroot" field provided. This can be useful if you have specific requirements for the directory structure of your application.
-
If any changes are required, the user can go back to the respective sections and make the changes. If everything looks good, they can click on the Create Application button to create the application. Your website should be live in the next 10-15 seconds. Once your application is installed, you will be redirected to an application dashboard from which you can manage the application.
Manual Pull
The Manual Pull feature allows you to manually pull the latest changes from the selected branch whenever needed. This feature works for both Private and Public repositories.
Step 1: Navigate to Created Application Dashboard → Git.
Step 2: Click on the Pull Latest Changes button to manually pull the latest changes from your selected branch.
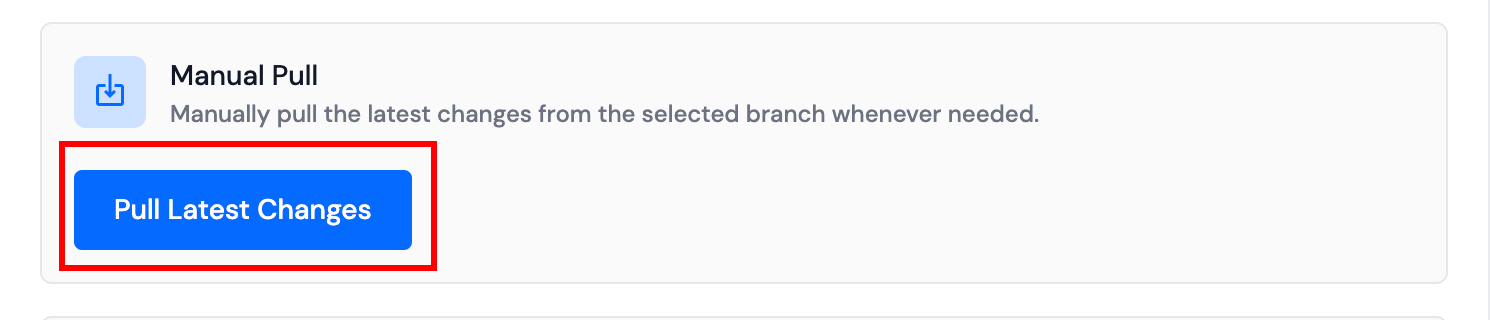
Step 3: After clicking the button, ServerAvatar will pull the latest changes from your repository's selected branch. If you have configured a deployment script, it will also run after the pull operation completes.
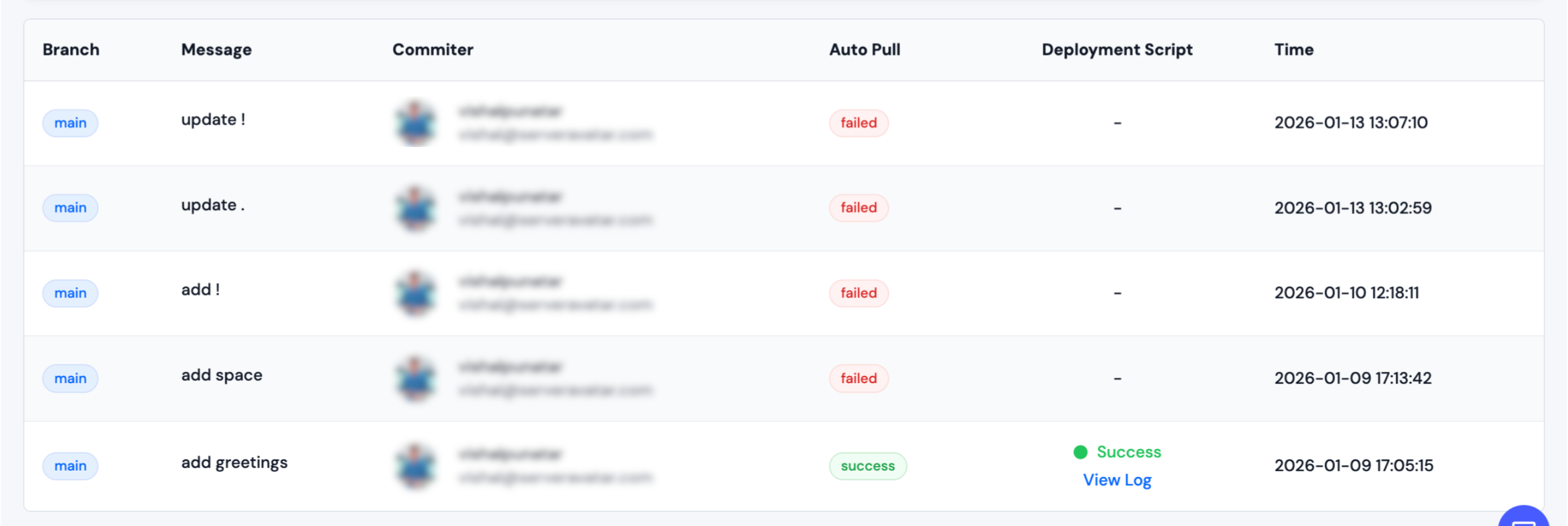
Auto Pull
You can not perform Enable Auto Pull if your repository Type is public.
Step 1: Navigate to Created Application Dashboard → Git.
Step 2: Then, click on Enable as shown in the image below.
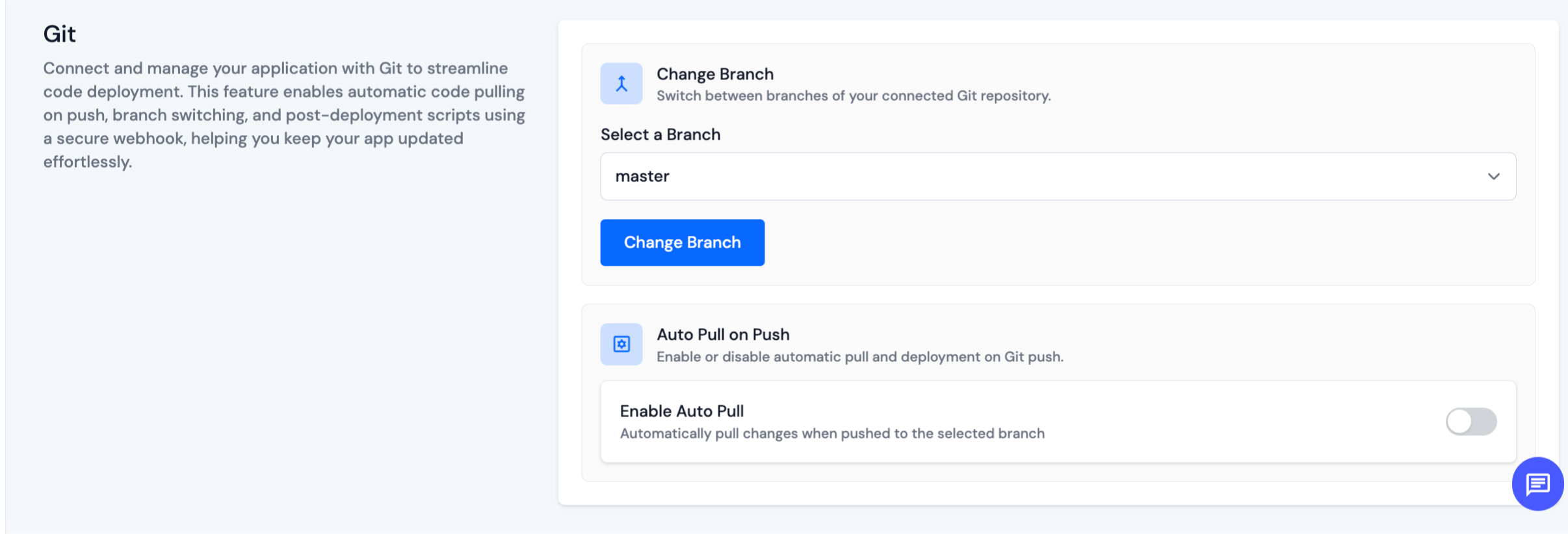
Step 3: After that, Copy Webhook URL.
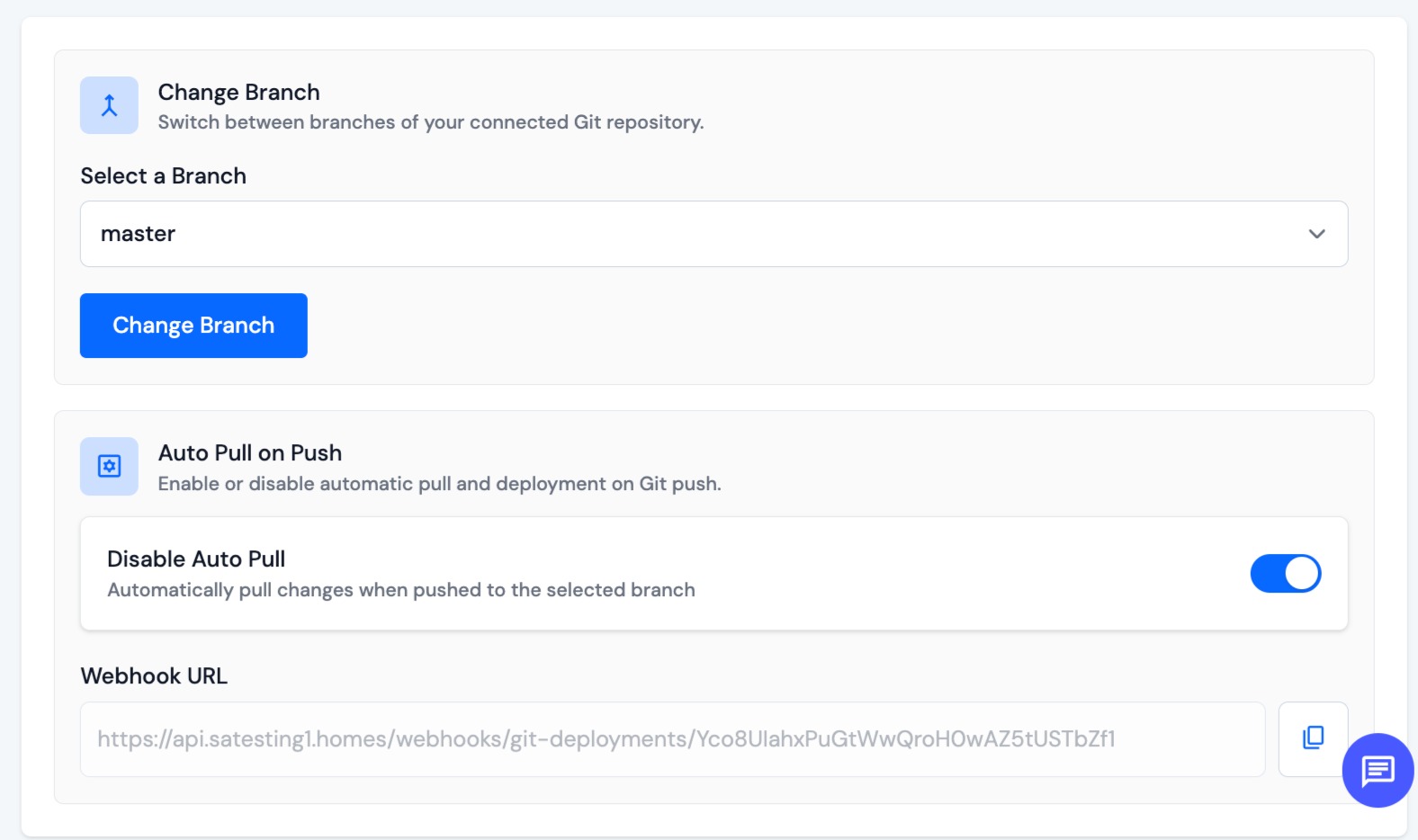
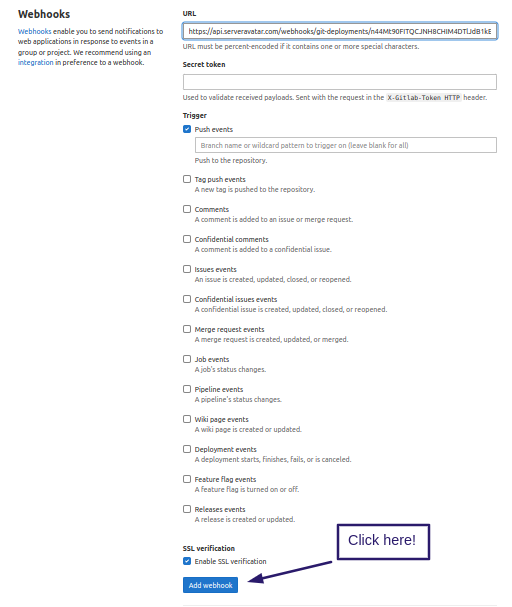
Step 4: Next, login to your Integrated Gitlab account, and In your Selected repository, navigate to Settings → Webhooks → Add webhook, and use the following settings:
- Payload URL: Your Copied Webhook URL
- Content Type: application/json
- SSL Verification: Disable (not recommended)
- Which events would you like to trigger this webhook?: Just the push event
- Active:: Check
Step 5: Click Add Webhook to save your settings, and the request should start working.
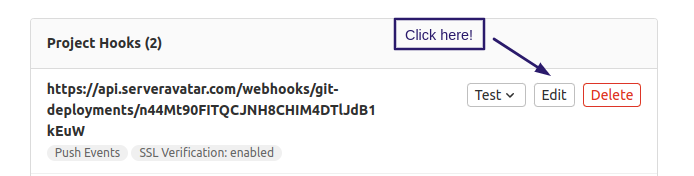
Step 6: Click on Edit, then click on Recent Deliveries tab for see your Request logs.
Step 7: You can see your commit history from the Webhook History section.
Change Branch
Step 1: Navigate to Created Application Dashboard → Git.
Step 2: Click on Change Branch and select the checkout branch.
Deployment Script
Step 1: Navigate to Created Application Dashboard → Git.
Step 2: If you want to run a Custom Script after a pull request, enter the script in the "Deployment Script" section and Save it.
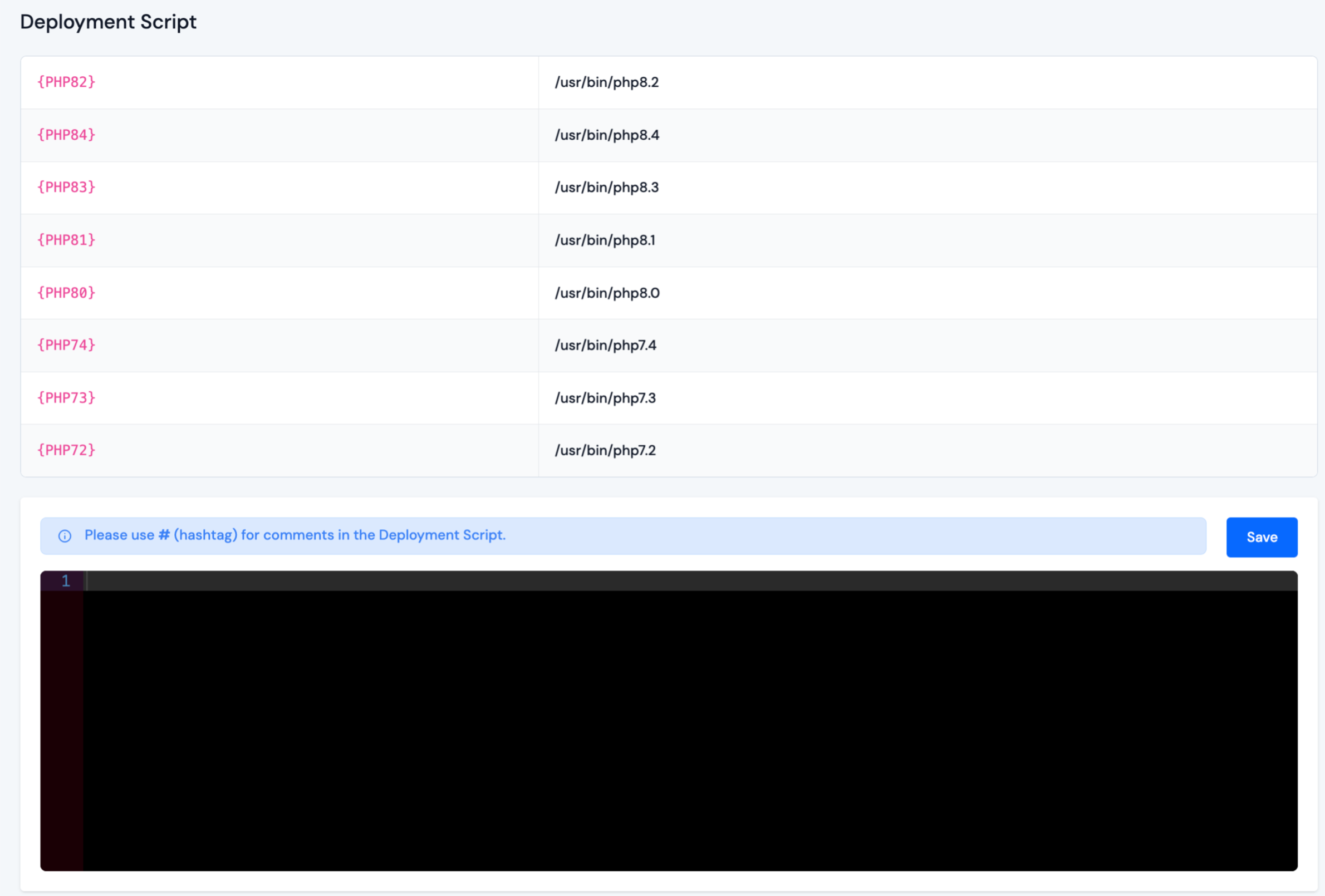
When the webhook receives a push request, you might want to run a Custom Script to clear some cache or upgrade your web application. You can write a script to do this command in the "Deployment Script" section.
Please use # (hashtag) for comment in Deployment Script.
The script will run inside your application root folder. If your deployment script includes composer and PHP command, it will use the default PHP-CLI. You must use a replacer to run a script using a different PHP version.
Replacer
-
The replacer is where you can tell the deployment script to run a specific PHP version.
-
For example:
{PHP70} artisan cache:clear -
Will be translated to this: /usr/bin/php7.0 artisan cache:clear
-
You can always type the full path to the PHP version if you don't want to use the replacer.